Finding your iPhone’s MAC address is easy once you know where to look. This unique code helps identify your device on networks and is needed for many Wi-Fi setups. To find your MAC address on an iPhone, go to Settings, tap General, select About, and scroll down to find the “Wi-Fi Address” – this is your MAC address.
Many people need to find this code when connecting to secure networks or troubleshooting connection problems. Your iPhone’s MAC address is like a digital fingerprint that routers use to recognize your device. Network administrators sometimes need this information to grant your iPhone access to their Wi-Fi networks.
How To Locate the MAC Address on Your iPhone
Your iPhone’s MAC address—short for Media Access Control address—is a unique identifier assigned to its Wi-Fi interface. It’s used by networks to recognize and manage your device. Whether you’re setting up MAC address filtering, assigning a static IP, or just need it for network troubleshooting, finding it is easy once you know where to look.
1. Find the MAC Address in iOS Settings
This is the most direct method. Every iPhone has its MAC address clearly displayed in the Settings app:
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Tap General.
- Tap About.
- Scroll down to find Wi-Fi Address — this is your iPhone’s MAC address.
It’s a string of 12 hexadecimal digits, usually separated by colons (e.g., D4:61:9D:6C:2B:57). This is the address your iPhone broadcasts when connecting to Wi-Fi, unless Private Address mode is enabled (more on that below).
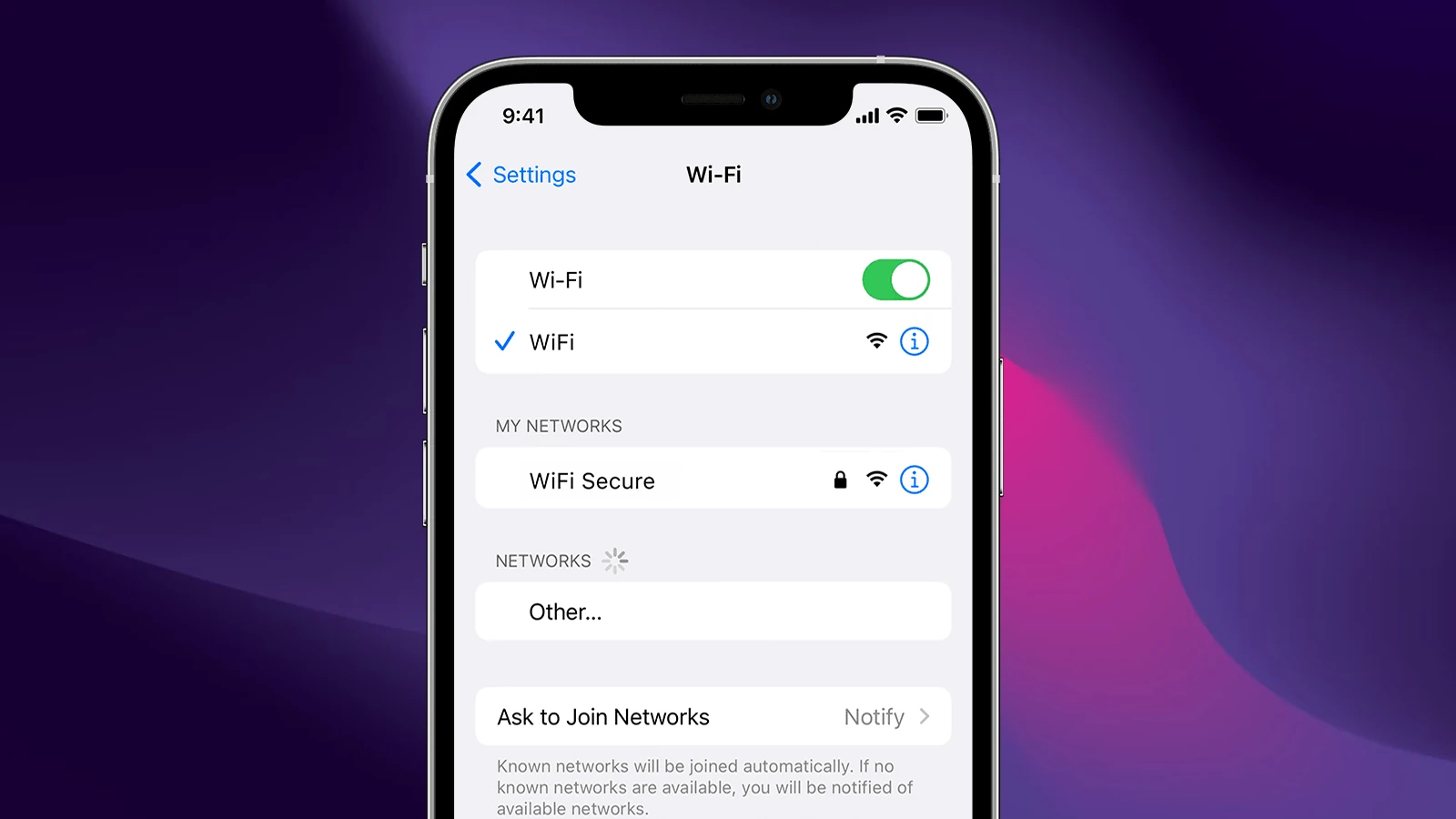
2. Check MAC Address for Specific Wi-Fi Networks
Starting with iOS 14, Apple introduced a privacy feature that randomizes your MAC address per network. So if you’ve enabled Private Wi-Fi Address, your iPhone will use a unique MAC address just for that network. To check it:
- Go to Settings > Wi-Fi.
- Tap the “i” icon next to the network you’re connected to.
- Look for Private Wi-Fi Address.
- The address listed here is the one being used specifically for this Wi-Fi network.
If Private Address is toggled on, the address will differ from the one in Settings > General > About. If you’re trying to whitelist your iPhone on a router, make sure you’re providing the address used for that particular network.
3. Disable Private MAC Address (If Necessary)
Some networks, especially enterprise or university networks, require your real hardware MAC address rather than the randomized private one. In these cases, you may need to disable the private address setting:
- Go to Settings > Wi-Fi.
- Tap the “i” icon next to the Wi-Fi network.
- Toggle Private Wi-Fi Address off.
- Reconnect to the network to start using your real MAC.
Once turned off, the MAC address you see in the About section will be the one in use.
4. Use iPhone’s MAC Address for Network Management
Knowing your iPhone’s MAC address can help with:
- MAC address filtering on routers for tighter security
- Static IP assignment for devices in home or office networks
- Device identification on corporate or guest networks
- Troubleshooting connection problems where hardware identifiers are required
Just remember, with MAC randomization now standard, you may have a different address for each network unless you’ve turned off the feature.
5. A Note About Bluetooth MAC Addresses
While most users only need the Wi-Fi MAC, your iPhone also has a separate MAC for Bluetooth. This isn’t shown in iOS settings, and Apple keeps it hidden for privacy. If you’re pairing with devices that require the Bluetooth MAC, you’ll need to retrieve it through specialized development tools like Xcode.
With these steps, you’ll always know how to find the right MAC address on your iPhone, whether you’re setting up a secure home network, registering your device with IT, or managing Wi-Fi connections on the go.
Key Takeaways
- The MAC address on an iPhone is listed as “Wi-Fi Address” in the Settings app under General > About
- Every iPhone has a unique MAC address that helps networks identify your specific device
- Finding your MAC address is essential for network security setups and solving Wi-Fi connection problems
Understanding MAC Addresses
MAC addresses serve as unique identifiers for network devices, playing a critical role in how devices communicate on local networks. They function as the physical address that helps route data to the correct device.
Definition
A MAC address (Media Access Control address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on a physical network. This hardware address consists of 12 hexadecimal digits (0-9, A-F), typically displayed in pairs separated by colons or hyphens.
For example, a MAC address might look like: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E
MAC addresses are:
- Permanently assigned by device manufacturers
- Unique to each network interface
- Embedded in the hardware of network adapters
Unlike IP addresses that can change, MAC addresses are meant to be fixed identifiers. However, modern devices can use private Wi-Fi addresses that change regularly for privacy.
Importance in Networking
MAC addresses are essential for basic network operations, particularly on Ethernet and Wi-Fi networks. They work at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model, below IP addresses.
Key functions include:
- Device identification – Networks use MAC addresses to identify devices uniquely on a local network
- Data delivery – Switches use MAC addresses to send data packets to the right device
- Network security – Many networks use MAC filtering to control which devices can connect
When a device joins a Wi-Fi network, it shares its MAC address with the router. The router then uses this address to direct traffic properly.
On iPhones, the Wi-Fi address shown in settings is the device’s MAC address. This address helps network equipment identify your phone when connected.
Locating the MAC Address on an iPhone
Finding your iPhone’s MAC address is simple once you know where to look. Your device’s MAC address (also called Wi-Fi address) can be found in two main places within your settings.
Via Wi-Fi Settings
The quickest way to find your MAC address is through your iPhone’s Wi-Fi settings. First, open the Settings app on your home screen. Tap on the Wi-Fi option near the top of the menu.
Make sure your Wi-Fi is turned on. You’ll see a blue “i” icon next to your connected network. Tap this information icon.
A new screen will appear with details about your connection. Scroll down and you’ll see Wi-Fi Address listed. This is your MAC address, shown as six pairs of letters and numbers separated by colons.
Through General Settings
Another way to find your MAC address is through the General settings. Open the Settings app on your iPhone. Scroll down and tap on General.
Next, select About at the top of the menu. This screen shows all the important information about your device.
Scroll down through this list until you find the entry labeled Wi-Fi Address. This string of numbers and letters is your iPhone’s MAC address.
The format typically looks like this: 00:11:22:AA:BB. You may need this address when connecting to certain networks or for network troubleshooting.
Comparative Guide for Other Devices
Finding your MAC address varies across different devices and operating systems. Each platform has its own unique path to locate this important network identifier.
On Android Devices
Android phones store MAC addresses in the Settings menu. To find yours:
- Open Settings on your Android phone
- Tap on About Phone (or About Device)
- Select Status or Hardware Info
- Look for “Wi-Fi MAC address” in the list
On some newer Android versions, you might need to tap Wi-Fi in Settings, then the gear icon next to your connected network. The MAC address appears there as “MAC address” or “Device MAC address.”
Android 10 and newer use private Wi-Fi addresses by default for better privacy. This means your phone might show both your actual MAC address and randomized ones used for different networks.
Samsung phones may require slightly different steps. Try looking in Settings > Connections > Wi-Fi > Advanced to find your MAC address.
Accessing MAC Address on iPad
Finding the MAC address on an iPad follows a similar process to iPhones:
- Open the Settings app on your iPad
- Tap on General
- Select About
- Scroll down until you see “Wi-Fi Address”
This “Wi-Fi Address” is your iPad’s MAC address. It appears as six pairs of letters and numbers separated by colons.
You can also find it through an alternate path:
- Go to Settings
- Tap Wi-Fi
- Press the “i” icon next to your connected network
- Your MAC address will show in the network details
iPads running newer iOS versions use private Wi-Fi addresses for enhanced privacy. You can toggle this feature in Settings > Wi-Fi > tap the “i” next to a network > Private Wi-Fi Address.
Finding MAC Address on Windows Computers
Windows computers offer several methods to locate MAC addresses:
Using Command Prompt:
- Press Windows key + R to open Run
- Type
cmdand press Enter - In Command Prompt, type
ipconfig /alland press Enter - Find “Physical Address” under your network adapter (it’s your MAC address)
Using Settings (Windows 8 and newer):
- Open Settings
- Select Network & Internet
- Click Status on the left panel
- Select View hardware and connection properties
- Look for your network adapter and find “Physical address (MAC)”
For a direct method, try the getmac command in Command Prompt. Just type getmac and press Enter to see all MAC addresses on your computer.
Locating MAC Address on Chromebooks
Chromebooks store MAC addresses in the system settings:
- Click on the time in the bottom-right corner
- Select the Settings gear icon
- Click on Wi-Fi in the left panel
- Select the network you’re connected to
- Look for “MAC Address” in the connection details
Alternatively:
- Open Chrome browser
- Type
chrome://systemin the address bar - Press Ctrl+F and search for “mac”
- Find your MAC address under “ifconfig” or “network_devices”
Chromebooks may also show the MAC address in the About section. Go to Settings > About Chrome OS > System to check hardware information including network details.
Remember that Chromebooks, like other modern devices, might use MAC randomization for privacy. Your actual hardware MAC address might differ from what’s shown for specific network connections.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
When your iPhone won’t connect to Wi-Fi networks, the problem often relates to either connectivity issues or MAC address settings. These common problems have specific solutions that can get you back online quickly.
Verifying Wi-Fi Connectivity
If your iPhone won’t connect to Wi-Fi, first check if the network is working. Try connecting another device to the same network to confirm it’s not a network-wide issue.
Restart your iPhone by turning it off and on again. This simple step often fixes connection problems by refreshing network settings.
Check if you’re within range of the Wi-Fi signal. Move closer to the router if needed. Walls and other obstacles can block signals.
Try resetting your network settings by going to Settings > General > Reset > Reset Network Settings. This will clear all saved Wi-Fi networks and passwords.
If nothing works, try restarting your router. Sometimes the issue is with the network equipment rather than your iPhone.
Ensuring Correct MAC Address Usage
Some networks use MAC filtering, which only allows devices with specific MAC addresses to connect. If your network uses this feature, you’ll need to find your iPhone’s MAC address and add it to the allowed list.
Your iPhone uses a feature called “Private Address” that can cause connection issues. This feature changes your MAC address to protect your privacy. To turn it off:
- Go to Settings > Wi-Fi
- Tap the info icon (i) next to your network name
- Toggle off “Private Address”
If using iOS 18 or later, you can choose between “Off,” “Fixed,” or “Rotating” privacy options. The “Fixed” option provides a good balance between privacy and compatibility.
Some networks require MAC registration for security. If your network administrator needs your MAC address, make sure you provide the correct one that your iPhone is currently using.
Advanced Topics
Beyond the basic methods, there are more technical ways to find and use your iPhone’s MAC address for network management and troubleshooting.
MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering adds an extra layer of security to your Wi-Fi network. This feature lets you control which devices can connect based on their MAC addresses.
To set up filtering on your router, you’ll need your iPhone’s Wi-Fi address from the Settings app. Most routers have this option in their admin panel under security settings.
Some benefits of MAC filtering include:
- Reduced unauthorized access to your network
- Better network management for homes and small offices
- Ability to prioritize specific devices
Remember that newer iPhones use MAC randomization by default. For filtering to work properly, you may need to disable this feature in your iPhone’s Wi-Fi settings by tapping the (i) icon next to your network name.
Finding MAC Address via Network Tools
Network administrators often need to find device MAC addresses without physical access to the iPhone.
Several tools can help identify MAC addresses on your network:
- Router admin pages – Check connected devices list
- Network scanner apps – Apps like Fing can scan and show all devices
- Command line tools – For computers on the same network
On a Mac, you can use Terminal with the command arp -a to see all devices. Windows users can use Command Prompt with ipconfig /all to view network details.
For corporate networks, more sophisticated tools like network monitors can track all connected devices. These tools show both the device name and its MAC address in real-time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Finding your iPhone MAC address is straightforward once you know where to look. Here are answers to common questions about locating and understanding MAC addresses on your iPhone.
How can you locate the MAC address in the iPhone’s settings?
The MAC address on an iPhone is listed as “Wi-Fi Address” in the settings menu. To find it, open the Settings app and tap on General. Then select About and scroll down until you see Wi-Fi Address.
This 12-character code is your device’s unique network identifier.
What steps are required to see the Wi-Fi MAC address on an iPhone?
Finding your iPhone’s MAC address takes just a few taps. First, open the Settings app from your home screen. Next, tap General, then About. Finally, scroll down to find the Wi-Fi Address entry.
The address appears as six pairs of numbers and letters separated by colons.
Is there a way to find the Bluetooth MAC address on an iPhone?
The Bluetooth MAC address isn’t directly visible in iPhone settings. Apple has limited access to this information for privacy reasons.
Some third-party apps claim to show this information, but they may not work due to Apple’s privacy restrictions.
Why does my iPhone display a different MAC address when connected to a router?
Your iPhone may show a different MAC address because of Apple’s Private Wi-Fi Address feature. This security feature generates a random MAC address for each network you join.
This helps protect your privacy by making it harder for networks to track your device across different locations.
What should I do to view my iPhone’s MAC address for a specific network?
To see the MAC address used for a specific network, go to Settings and tap Wi-Fi. Next, tap the info icon (i) next to the connected network name.
Look for “Private Wi-Fi Address” on this screen. If it’s enabled, this shows the unique MAC address used for this network.
How can I check if my iPhone is using a private MAC address?
To check if your iPhone uses a private MAC address, open Settings and tap Wi-Fi. Tap the info icon (i) next to your connected network.
Look for the “Private Wi-Fi Address” toggle. If it’s on, your iPhone is using a random MAC address instead of your device’s actual Wi-Fi address for this network.