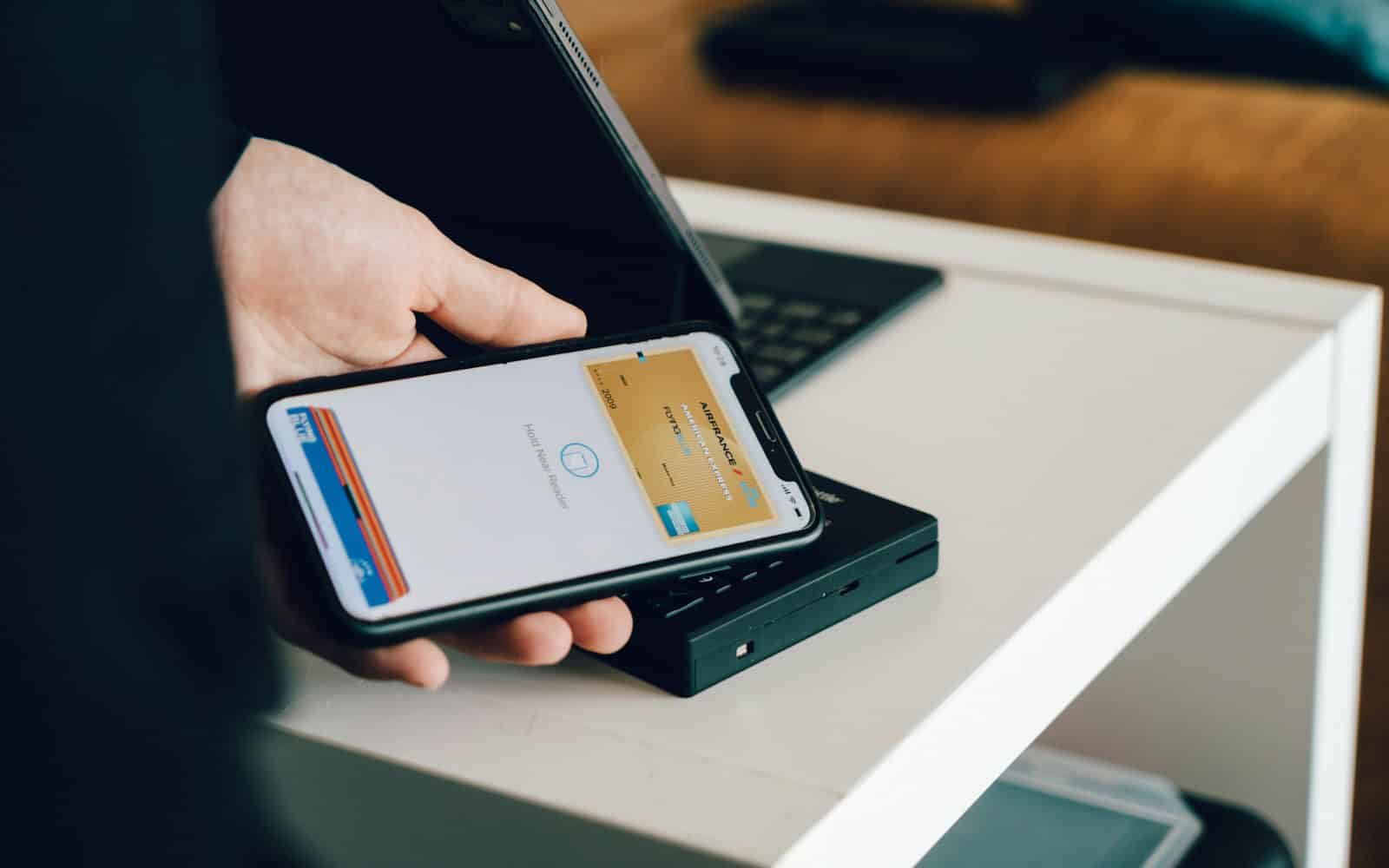
In an era where contactless payments have become the norm, concerns about security are natural. Is tapping your phone really safer than swiping your card? When it comes to Apple Pay, the answer is a strong yes. Apple Pay has emerged as one of the most secure digital wallets available today, combining cutting-edge encryption, biometric verification, and real-time monitoring to protect users from fraud.
Let’s take a closer look at why Apple Pay remains one of the most trusted payment platforms in 2025—and what steps you can take to further safeguard your digital wallet.
🔐 Why Apple Pay Is Considered Extremely Secure

1. Tokenization and Encryption
Every time you add a credit or debit card to Apple Pay, the actual card number is never stored on your device or Apple’s servers. Instead, a unique “Device Account Number” is assigned and encrypted. During each transaction, Apple Pay generates a dynamic security code specific to that transaction, ensuring your real card data is never exposed.
2. Biometric Authentication
To complete a payment, Apple Pay requires Face ID, Touch ID, or a secure passcode. Even if a thief gets hold of your iPhone or Apple Watch, they can’t make a purchase without biometric verification. This is a significant upgrade over traditional cards, which can be swiped or used online with just basic information.
3. Secure Element & Hardware Isolation
Apple Pay stores your encrypted payment credentials in a dedicated chip known as the Secure Element. This chip operates independently of the main operating system and cannot be accessed by other apps or iOS processes, drastically minimizing the risk of data breaches or malware interference.
4. Private by Design
Apple doesn’t track what you buy, where you buy it, or how much you spend. Your transactions remain between you, the merchant, and your bank. This commitment to privacy is a fundamental part of Apple’s ecosystem.
🛡️ Apple Pay’s Built-In Fraud Protection
1. Real-Time Notifications
Each transaction made with Apple Pay triggers an instant notification, allowing you to review charges as they happen. This real-time insight enables swift action if suspicious activity occurs.
2. Remote Disabling via Find My App
Lose your phone or watch? You can remotely disable Apple Pay using the Find My app or by logging into iCloud. This halts all payment capability without needing to cancel your cards.
3. Advanced Fraud Protection for Apple Card
If you use the Apple Card through Apple Pay, you can enable Advanced Fraud Protection. This rotates the card’s security code (CVV) periodically, which adds an extra barrier for online purchases where Apple Pay isn’t accepted.
4. Purchase Disputes and Chargeback Support
Apple Pay integrates seamlessly with your existing bank or credit card protections. If you’re charged fraudulently, the same dispute and refund policies apply.
⚠️ Common Risks and How to Avoid Them
While Apple Pay is incredibly secure, social engineering and user error remain potential vulnerabilities. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Phishing Attacks: Be wary of fake emails, texts, or phone calls pretending to be from Apple or your bank. Never click links or share sensitive info unless you’re sure of the source.
- Public Wi-Fi Dangers: Avoid setting up Apple Pay or inputting sensitive information while connected to unsecured networks.
- Social Engineering Scams: Scammers may pose as Apple Support or financial institutions to trick you into revealing personal details. Always verify credentials through official channels.
✅ Best Practices to Maximize Apple Pay Security
- Enable Biometric Authentication: Use Face ID or Touch ID rather than relying solely on a passcode.
- Keep iOS Up to Date: Regular iOS updates patch security vulnerabilities and improve protection.
- Review Transaction History Frequently: Check your Apple Pay activity or bank statements for unauthorized activity.
- Use Strong Passcodes: Avoid simple codes like “123456” or birth dates. Choose a complex, unique passcode.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication for Apple ID: This protects your entire Apple ecosystem—including Apple Pay—from unauthorized access.
📌 Final Thoughts
In 2025, Apple Pay continues to lead the digital wallet space in both convenience and security. From its secure hardware-based architecture to privacy-first principles, Apple has built a system that offers greater peace of mind than most traditional payment methods. By combining Apple’s layered security with your own best practices, you can confidently use Apple Pay in stores, apps, and online—without worrying about your sensitive data falling into the wrong hands.
Key Takeaways
- Apple Pay uses unique tokens instead of your real card number for better security than physical cards.
- Every payment needs your fingerprint, face scan, or passcode, so others can’t use your phone to pay.
- You can quickly lock or erase your Apple Pay data if your phone is lost or stolen.
Understanding Apple Pay
Apple Pay offers a secure way to make payments without carrying physical cards. This digital wallet system uses built-in security features to protect your information when shopping.
What Is Apple Pay?
Apple Pay is a digital wallet service created by Apple Inc. It lets users make payments using their iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, or Mac.
The service stores your credit and debit card information safely on your device. When you pay, your actual card numbers aren’t shared with merchants.
Instead of pulling out a physical card, you can simply hold your device near a payment terminal. Apple Pay works at millions of stores and restaurants worldwide.
You can also use Apple Pay for in-app purchases and website payments. This makes checkout faster and more secure than typing your card details each time.
How Apple Pay Works
Apple Pay uses Near Field Communication (NFC) technology to connect with payment terminals. This allows for quick contactless payments without touching the payment device.
When setting up Apple Pay, your card details are converted into a unique device number. This number is encrypted and stored in a special chip called the Secure Element.
The payment process is simple:
- Open Apple Pay on your device
- Verify your identity with Face ID, Touch ID, or passcode
- Hold your device near the payment terminal
Your phone sends a one-time code instead of your actual card number. This dynamic security code changes with each purchase, making it harder for thieves to steal your information.
Transactions happen in seconds, making checkout fast and easy.
Security Features of Apple Pay
Apple Pay comes with powerful security measures built right into your device. These features work together to protect your card information and keep your payments private.
Authorization Mechanisms
Apple Pay uses biometric security like Face ID or Touch ID to verify it’s really you making a purchase. This adds a strong layer of protection that physical cards don’t have.
When you pay, you must confirm with your face, fingerprint, or passcode. This means even if someone steals your phone, they can’t use Apple Pay without your unique identifiers.
Some banks add two-factor authentication when you first add a card. This extra step sends a code to your phone or email that you must enter to confirm it’s really you.
The multi-step verification process makes Apple Pay much harder to hack than a regular credit card.
Tokenization Process
Apple Pay uses a clever system called tokenization to protect your card details. Instead of sharing your actual card number with stores, it creates a unique device account number.
This number is stored on your device in a special secure area. When you make a payment, Apple Pay creates a one-time transaction code that works only for that purchase.
This approach means stores never see your real card number. Even if a merchant’s system gets hacked later, criminals won’t have access to your actual card details.
Tokenization makes Apple Pay one of the safest payment methods available today because your true card number stays hidden.
Apple’s Secure Element
The heart of Apple Pay’s security is the Secure Element. This is a special chip in your iPhone or Apple Watch that’s separate from the rest of your device’s system.
The Secure Element stores your sensitive payment data in encrypted form. This chip is designed with one job: keeping financial information safe.
It’s physically isolated from the main processor. This means even if malware infects your phone, it can’t reach the payment data.
When you make a purchase, the Secure Element creates the special transaction codes without exposing your card details. This hardware-based approach gives Apple Pay stronger protection than purely software solutions.
Privacy and Data Protection
Apple Pay combines high security standards with strong privacy protections. The system is built to keep your personal data safe while maintaining the convenience of digital payments.
Anonymity of Transactions
Apple Pay creates a unique level of privacy during payments that physical cards can’t match. When you pay with Apple Pay, the store never sees your actual card number. Instead, they get a device-specific number and a one-time code that works only for that purchase.
Your transaction details stay private too. Apple doesn’t know what you bought, where you bought it, or how much you paid. This makes Apple Pay more private than regular credit cards, which often track spending habits.
However, it’s worth noting that Apple Pay isn’t completely anonymous. Your bank still knows about your purchases, just like with regular card transactions.
Apple’s Privacy Policy
Apple’s approach to payment privacy follows its broader company values. According to Apple Pay’s privacy documentation, they use encryption to protect your payment information when it’s sent through apps or websites.
Your Apple ID is linked to your Apple Pay account, but Apple keeps this connection secure. They don’t share your Apple ID details with merchants when you make payments.
Apple designed their payment system with privacy in mind, making sure your card numbers and identity aren’t shared with stores. This reduces the risk of data breaches affecting your financial information.
Apple Pay isn’t just a feature—it’s a set of privacy-focused technologies that work together to protect your information while making payments more convenient.
Using Apple Pay Safely
Apple Pay gives you a secure way to pay in stores and online. Following a few key safety steps can help protect your money and personal information when you use this payment system.
Best Practices for Consumers
Setting up Apple Pay properly is your first line of defense. Always use strong passcodes on your devices rather than simple 4-digit PINs. Enable Face ID or Touch ID to add an extra layer of security to your payments.
Never add payment cards to Apple Pay while connected to public Wi-Fi networks. These networks can be monitored by hackers looking to steal your information. Instead, use your cellular data or a trusted home network.
Apple Pay creates a device-specific number for each card you add. This means your actual card numbers aren’t stored on your device or shared with merchants. This system helps keep your financial details private.
Regularly check your transaction history in the Wallet app. Look for any payments you don’t recognize. If you spot something suspicious, report it to your bank immediately.
Preventing Unauthorized Purchases
If your iPhone or Apple Watch is lost or stolen, activate Lost Mode through Find My immediately. This locks your device and prevents anyone from using Apple Pay without your authentication.
Remember that Apple Pay requires your fingerprint, face scan, or passcode for every transaction. Never share these security details with anyone, even friends or family members you trust.
Consider setting up transaction alerts with your bank. These notifications can alert you to any Apple Pay purchases in real time, allowing you to spot fraud quickly.
For added protection, Apple Pay doesn’t store your actual card details on your device. Instead, it uses encrypted tokens that hackers can’t decode, making your payment information significantly more secure than physical cards.
Lost or Stolen Devices
If your iPhone is lost or stolen, Apple provides tools to protect your Apple Pay information and keep your money safe. These features work quickly to block access to your accounts.
Activating Lost Mode
Lost Mode is a key security feature for stolen iPhones. When enabled, it locks your device with your passcode and disables Apple Pay completely.
To turn on Lost Mode:
- Go to iCloud.com on any device
- Sign in with your Apple ID
- Click on “Find iPhone”
- Select your missing device
- Click “Lost Mode”
Lost Mode prevents anyone from using your cards in Apple Pay. The thief cannot make purchases even if they try to use your phone at a payment terminal.
Your credit and debit card numbers stored in the Wallet app aren’t actually on your device. Apple Pay uses special numbers and codes for each transaction instead of your real card details.
Using Find My iPhone
Find My iPhone helps track and protect your device when it’s missing. This app shows your iPhone’s location on a map and offers several security options.
To use Find My iPhone:
- Open the Find My app on another Apple device
- Sign in with the same Apple ID
- View your device’s current or last known location
- Play a sound to help find a nearby device
- Erase your iPhone remotely if needed
Remote erase is especially important for Apple Pay security. When you erase your device, all your personal information including payment details is removed. This happens even if the iPhone isn’t connected to the internet at that moment.
Apple’s system is designed so that Apple Pay cannot be used after you’ve reported your device as missing. Your privacy and financial information remain protected.
Apple Pay and Traditional Payment Methods
Apple Pay offers key security advantages over traditional payment methods. It uses special technology to keep your money and card details safer than regular cards when you shop.
Comparison with Debit and Credit Cards
Apple Pay is considered safer than using physical credit and debit cards. The main reason is that Apple Pay doesn’t store actual card numbers on your device.
Instead, it creates unique codes (tokens) for each transaction. This means your real card number is never shared with stores when you pay.
When someone uses a regular card, the card number gets passed to the payment system. This creates more chances for thieves to steal your information.
With Apple Pay, even if a store’s payment system gets hacked, your card details stay safe. Hackers would only get the one-time code, which is useless for other purchases.
Your financial information remains protected since Apple Pay keeps it in a secure part of your phone that apps can’t access.
Benefits over EMV Chips and Magnetic Stripes
EMV chips improved security over magnetic stripes, but Apple Pay takes it further. Magnetic stripe cards are easy to copy with cheap card skimmers that thieves attach to card readers.
While EMV chips are harder to copy, they still show your card number to merchants. Apple Pay avoids this risk by never sharing your actual card details.
Apple Pay adds extra security through your phone’s lock methods. You must use Face ID, Touch ID, or a passcode to approve payments, making it nearly impossible for others to use your wallet.
Contactless payments through Apple Pay are faster than inserting chip cards. You can pay with a quick tap rather than waiting for chip processing.
For online shopping, Apple Pay is more secure because you don’t need to type card numbers on websites where they might be stolen. The system is built with multiple security layers that work together to keep your money safe.
Future of Payment Security
Digital payment security continues to evolve with new technologies and threats. The landscape is shifting toward more robust protection systems while maintaining convenience for users.
Advancements in Digital Security
Payment security technology is growing more sophisticated every day. End-to-end encryption has become standard for services like Apple Pay, making transactions much harder to intercept.
Biometric authentication is replacing traditional passwords. Fingerprints and facial recognition provide stronger security while being easier to use than remembering complex passwords.
Multi-factor authentication is becoming more common for digital wallets. This means users need to provide two or more verification methods before completing a transaction.
AI-powered fraud detection systems can now spot unusual patterns in spending habits. These systems alert users instantly when suspicious activity occurs on their accounts.
Dynamic security codes are replacing static card numbers. Every transaction uses a unique code, making stolen information useless for future purchases.
Beyond Apple Pay
The future of payment security extends beyond any single platform. Apple ID is becoming increasingly important as identity verification becomes central to financial transactions.
Blockchain technology offers promising advances in payment security. It creates unchangeable records of transactions that can’t be altered by hackers.
Contactless payments are expanding beyond phones to wearable devices. Smart watches, rings, and even clothing may soon contain secure payment technology.
Open banking standards are changing how financial data is shared. These standards give users more control over their information while maintaining security.
Virtual private networks are becoming essential tools for secure online shopping. They encrypt internet connections when making payments on public networks.
Anti-phishing measures continue to improve as digital wallets become more common. Companies are educating users about security habits and implementing automated protections against fake websites and apps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Apple Pay offers multiple security layers to protect your financial information during transactions. These features work together to prevent fraud and keep your data safe.
What measures does Apple Pay implement to prevent hacking?
Apple Pay uses built-in security features in both hardware and software to protect transactions. It doesn’t store card details on your device.
Instead, it creates encrypted tokens that are sent to your bank when you pay. This means your actual card numbers are never shared with merchants or stored on Apple servers.
Apple Pay requires Face ID, Touch ID, or a passcode to confirm transactions, adding an extra layer of security.
Can Apple Pay securely handle transactions with unknown parties?
Yes, Apple Pay can handle transactions with unknown parties safely. When you pay, merchants never see your actual card number.
They only receive a one-time payment token specific to that transaction. This protects your card information even when dealing with new or unfamiliar businesses.
Your identity is never shared with merchants, which adds another level of privacy protection.
Are online purchases using Apple Pay protected against fraud?
Online purchases with Apple Pay have strong fraud protection. The system uses device-specific numbers and unique transaction codes instead of your actual card details.
This means even if a website’s payment system is compromised, hackers can’t get your real card information. Many banks also offer additional fraud protection for Apple Pay transactions.
You should still avoid using Apple Pay on unsecured Wi-Fi networks when making online purchases.
How does Apple Pay safeguard users against skimming devices?
Apple Pay is highly effective against skimming devices. Since your phone never transmits your actual card number, skimmers can’t capture usable payment information.
The NFC (Near Field Communication) technology used by Apple Pay is more secure than magnetic strips on physical cards. Each transaction uses a unique code that works only once.
This makes the data useless to thieves even if they somehow intercept the transmission during payment.
What are the risks, if any, associated with using Apple Pay?
The main risks with Apple Pay relate to device security rather than the payment system itself. If someone gains access to your phone and knows your passcode, they could potentially make payments.
Setting up secure passcodes and using Face ID or Touch ID helps minimize this risk. Lost or stolen devices should be locked or wiped remotely using Find My iPhone.
Phishing attempts trying to trick you into adding cards to fake Apple Pay setups are another potential risk.
How does the security for Apple Pay transactions with debit cards work?
Debit card transactions through Apple Pay work similarly to credit cards. Your actual debit card number is replaced with a device-specific number.
Each payment uses a unique transaction code that works only once. This means your debit card details stay protected during transactions.
Multiple layers of protection are built into the system to keep your bank account secure while offering the convenience of contactless payments.