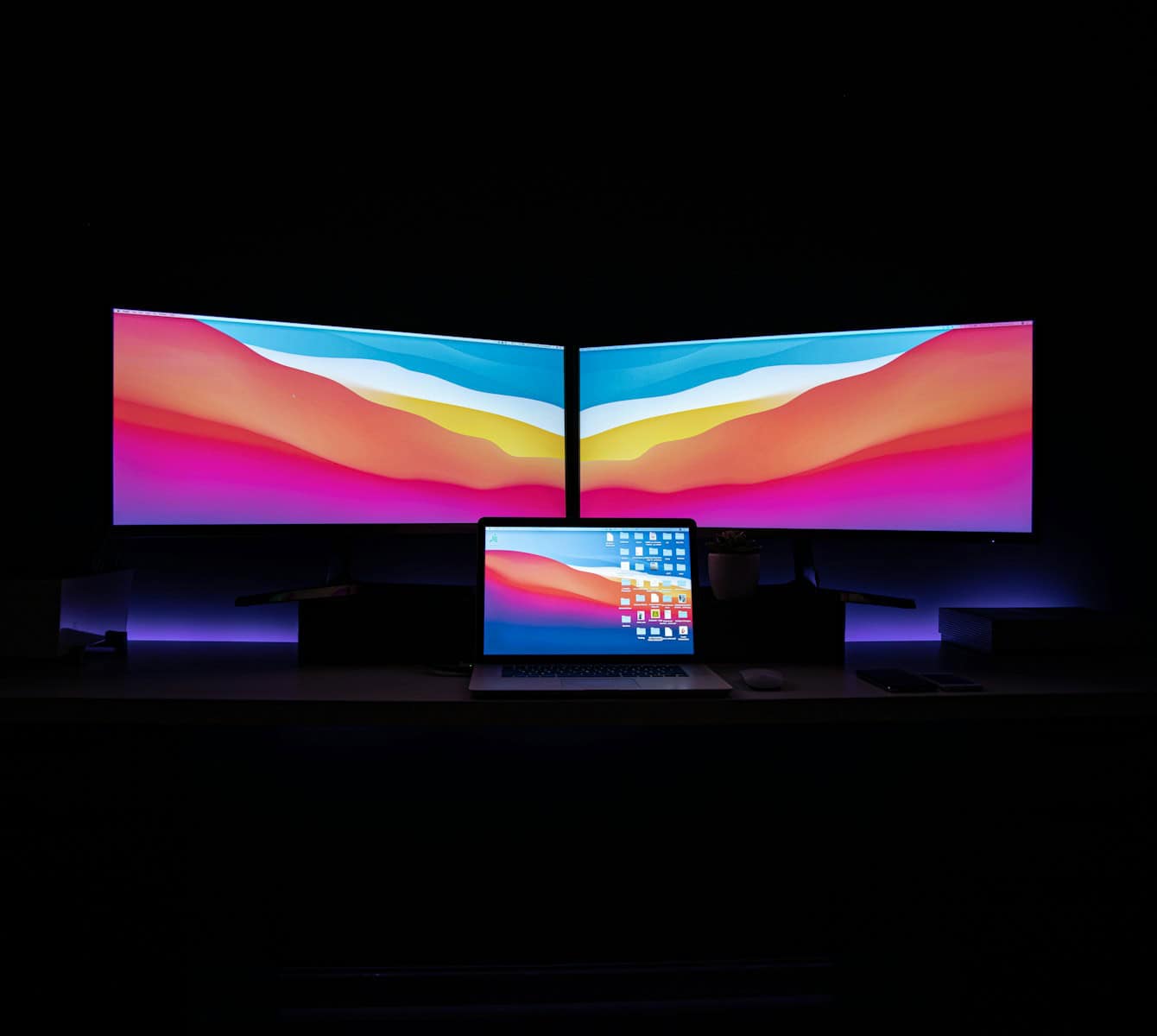
Adding a second monitor to your Mac can boost your work setup. It gives you more screen space to spread out your work and see more at once. You can connect an external monitor to any Mac by using the right cable or adapter for your specific model and adjusting a few settings to make it work perfectly. This simple upgrade can make a big difference in how you use your computer every day.
Getting your monitor and Mac to work together is easier than you might think. First, check what ports your Mac has and what connection your monitor uses. Most newer Macs need a Thunderbolt or USB-C cable to connect to displays, while older models might use HDMI or DisplayPort. Once connected, your Mac should spot the new screen right away, but you can fine-tune how they work together in the Displays section of System Settings.
How to Connect an External Monitor to a Mac Computer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Connecting an external monitor to your Mac can expand your workspace, improve productivity, and enhance your viewing experience. Here’s how to set it up easily.
Step 1: Check Your Mac’s Ports
- Identify the video output ports on your Mac. Common ports include:
- Thunderbolt 3 / USB-C
- HDMI
- Mini DisplayPort
- DisplayPort
- Check your external monitor’s input ports (HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, DVI).
- You may need an adapter (e.g., USB-C to HDMI) depending on the ports available.
Step 2: Connect the Monitor
- Turn off your Mac and monitor (recommended but optional for most Macs).
- Connect the external monitor to your Mac using the appropriate cable and adapter.
- Turn on the monitor and then your Mac.
Step 3: Configure Display Settings
- On your Mac, open System Settings (or System Preferences).
- Go to Displays.
- Your Mac should detect the external monitor automatically.
- Choose how to use the display:
- Mirror Displays: Shows the same content on both screens.
- Use as Separate Display: Extends your desktop for more workspace.
- Arrange the displays by dragging them to match their physical layout.
- Adjust resolution, brightness, and color settings as needed.
Step 4: Use Your External Monitor
- You can now drag windows between your Mac’s screen and the external monitor.
- Close your MacBook lid to use only the external monitor (clamshell mode) if you have an external keyboard and mouse connected.
Tips
- For best performance, use high-quality cables and adapters.
- If the monitor isn’t detected, try unplugging and reconnecting or restarting your Mac.
- Some Macs support multiple external monitors; check your model’s specifications.
For more detailed instructions and troubleshooting, see Apple’s official guide on Connect a display to your Mac.
Key Takeaways
- Connect your monitor with the right cable for your Mac model and adjust settings in System Settings under Displays.
- External monitors work with all Mac computers including MacBooks that can be used in closed clamshell mode.
- Use multiple monitors to increase workspace and boost productivity with simple drag-and-drop window management.
Essential Requirements
Before connecting an external monitor to your Mac, you need the right equipment and knowledge about your computer’s ports. Understanding your Mac model and the types of connections available will make setup much easier.
Identify Mac Model and Compatible Monitors
First, check which Mac model you have. Different Macs have different ports. To find your Mac model, click the Apple menu and select “About This Mac.”
MacBook Pro models from 2016-2020 typically have only Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C) ports. Newer M1/M2 MacBook Pro models may include an HDMI port alongside Thunderbolt ports.
MacBook Air computers usually have limited ports – newer models use Thunderbolt/USB-C while some M2 versions include an HDMI port.
iMac, Mac mini, and Mac Studio usually offer more connection options, including USB-C, Thunderbolt, DisplayPort, and HDMI.
For monitor compatibility, check these specs:
- Resolution support
- Refresh rate
- Color space (P3, sRGB)
Your Mac can connect to various display types as long as you have the right cables or adapters.
Types of Monitor Connectors and Adapters
The most common monitor connections for Macs include:
USB-C/Thunderbolt: Modern Macs use these ports for video output. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 can transfer video, audio, data, and power through a single cable. They support connecting multiple displays with the right setup.
HDMI: Directly connects to TVs and many monitors. Some newer Mac models include an HDMI port.
DisplayPort: Common on professional monitors, offering high resolution and refresh rates.
VGA/DVI: Older standards that require adapters for Mac connection.
Adapters you might need:
- USB-C to HDMI
- USB-C to DisplayPort
- USB-C to DVI
- Thunderbolt to HDMI
When buying adapters, make sure they support your monitor’s resolution and refresh rate. Apple and third-party adapters vary in quality and connection reliability. For best results, use high-quality cables and adapters.
Setting Up the External Monitor
Connecting an external monitor to your Mac involves both physical connections and software configuration. Getting the setup right ensures you’ll enjoy the full benefits of your additional screen space.
Physical Connection of the Monitor
First, identify which video ports your Mac has available. Most modern Macs come with either USB-C, Thunderbolt, or HDMI ports.
For newer MacBook models with only USB-C/Thunderbolt ports, you’ll need the right adapter or cable:
- USB-C to HDMI adapter for HDMI monitors
- USB-C to DisplayPort cable for DisplayPort monitors
- Thunderbolt 3 to Thunderbolt 2 adapter for older displays
Make sure both your Mac and monitor are powered off before connecting them. This prevents any potential power surges that might damage either device.
Once you have the right cable, simply plug one end into your Mac and the other into your monitor. Turn on the monitor first, then your Mac, which should automatically detect the new display.
Configuring Mac System Preferences
After the physical connection is made, your Mac should detect the monitor automatically. If not, you may need to adjust settings.
Open System Settings (or System Preferences) from the Apple menu, then click on Displays. Here you can configure how your monitors work together:
Display Arrangement options:
- Mirror Displays: Shows the same content on both screens
- Extended Desktop: Treats the external monitor as additional screen space
You can drag the display icons to match their physical arrangement. This helps with mouse movement between screens. The white menu bar shows which display is set as the main one.
Adjust resolution and refresh rate settings for best quality. For many external monitors, selecting “Default for display” gives optimal results. You can also customize brightness, color profile, and rotation to suit your needs.
Using Your Mac in Clamshell Mode
Clamshell mode lets you use your MacBook with the lid closed while connected to an external monitor. This setup creates a cleaner desktop experience and can help prevent overheating.
Activating Clamshell Mode
To use your Mac in clamshell mode, you need to follow a few simple steps. First, connect your external display to your MacBook. Then plug in an external keyboard and mouse or trackpad. These accessories are necessary because you won’t be able to use your laptop’s built-in keyboard or trackpad when it’s closed.
Next, make sure your MacBook is connected to a power source. With everything connected, you can close the lid of your MacBook. The display should automatically switch to your external monitor.
If your Mac goes to sleep when you close it, you may need to adjust some settings. Under System Settings > Displays > Advanced, look for an option to prevent the Mac from automatically sleeping when the display is closed.
For macOS Ventura users who experience issues, a common workaround involves disabling the sleep when plugged in setting before closing the lid.
Best Practices for Clamshell Mode
To get the most from clamshell mode, position your MacBook on a stand or cooling pad. This helps with airflow and prevents overheating during extended use. Some users prefer dedicated laptop stands like those from SVALT that are designed for clamshell setups.
Make sure your MacBook has enough ventilation. The computer still generates heat even when closed, so good airflow is important.
Power settings to check:
- Power adapter is connected
- Auto sleep is disabled when lid is closed
- Display settings are configured for your external monitor
If you’re using multiple monitors, arrange them in System Settings > Displays to match their physical layout on your desk. This makes cursor movement between screens feel natural.
Remember to properly wake or shut down your Mac. Press any key on your external keyboard to wake it up. To shut down, use the Apple menu rather than just unplugging.
Multi-Monitor Setup and Management
Setting up multiple monitors with your Mac enhances productivity and creates a more versatile workspace. With the right connections and settings, you can customize your displays to suit various professional needs.
Connecting Multiple External Monitors
Most Mac computers can support two or more external displays depending on your model. For newer Macs with USB-C or Thunderbolt ports, you’ll need the right adapters or docking stations to connect multiple monitors.
MacBook Pro models with M1 Pro or M1 Max chips can connect to multiple displays directly through their Thunderbolt ports. Older Macs might need a DisplayLink adapter to support more than one external monitor.
To connect a second monitor:
- Plug the display into an available Thunderbolt/USB-C port
- Use appropriate adapters for HDMI or DisplayPort connections
- For more than two displays, consider a Thunderbolt dock or DisplayLink technology
Make sure your Mac has restarted after connecting all displays. This helps the system recognize and configure each display properly.
Arranging Display Layout
Once your monitors are connected, you’ll need to arrange them correctly. Open System Settings and select Displays to access display management options.
In the display settings, you can:
- Drag the display icons to match your physical setup
- Choose which display serves as your main monitor
- Set different resolutions for each screen
- Enable or disable display mirroring
For productive setups, most users extend their displays rather than mirroring them. This gives you more screen space rather than showing the same content on all screens.
You can also use Mission Control to manage windows across multiple displays and create separate workspaces on each monitor, increasing your working area and organization.
Advanced Display Settings for Professionals
Professional users often need precise display settings for color-critical work. Mac offers several advanced options to optimize your multi-monitor experience.
For color professionals:
- Color calibration: Use the built-in calibration assistant or professional calibration tools
- Color profiles: Select or create custom profiles for each display
- True Tone: Disable for color-accurate work
You can also adjust refresh rates and resolutions for each display separately. Video editors might set one monitor to preview video at a specific frame rate while keeping another at standard settings.
Some professionals use display arrangement to create specialized workspaces—placing coding windows on one display, reference materials on another, and communication tools on a third. This setup maximizes efficiency for complex workflows.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When your Mac won’t connect with an external monitor, several common problems might be causing the issue. Finding and fixing these issues requires checking both hardware connections and software settings.
Connectivity and Video Signal Problems
First, check all your cables and adapters. Make sure cable connections are secure between your Mac and the monitor. Try unplugging and reconnecting all cables.
Inspect your cables for damage. Frayed or bent cables often cause display problems. If possible, test with a different cable to see if that resolves the issue.
Try different ports on your Mac. Some ports might work while others don’t. For Macs with multiple USB-C ports, not all may support video output equally.
Check if your adapter is compatible with your Mac model. Apple computers often need specific adapters for different display connections. HDMI adapters need to match your Mac’s specifications.
Port reset technique: Unplug all accessories from your Mac, wait 10 seconds, then reconnect only the monitor cable. This can reset the connection and fix signal problems.
Software and Compatibility Issues
Update macOS to the latest version. Many display issues are fixed in newer software updates, especially with macOS Monterey and Ventura.
Adjust display settings properly:
- Go to Apple menu → System Settings → Displays
- Check if “Mirror Displays” is enabled or disabled as needed
- Try changing resolution settings if the display appears but looks wrong
Reset NVRAM/PRAM by:
- Shut down your Mac
- Turn it on and immediately press Option + Command + P + R
- Hold these keys for 20 seconds
- Release when you hear the startup sound or see the Apple logo
For DisplayLink devices, make sure you have the latest DisplayLink Manager software installed. This is essential for proper external display functionality.
Monitor Not Detected or Working
If your Mac isn’t detecting the monitor at all, try putting your Mac to sleep and waking it. Sometimes this triggers display detection.
Check monitor power and settings. Make sure the monitor is powered on and set to the correct input source. Try pressing the input select button on your monitor.
Reset your monitor to factory settings using its built-in menu. This can clear any configuration issues preventing detection.
For multiple monitors, try connecting just one. Sometimes connection issues occur when too many displays are connected simultaneously.
Quick fix checklist:
- Restart both your Mac and monitor
- Try a different display if available to determine if your monitor is faulty
- Connect your Mac to a TV via HDMI as a test
- Boot your Mac in Safe Mode to check if software conflicts are causing issues
Use System Information (Apple menu → About This Mac → System Report → Graphics/Displays) to verify if your Mac detects the monitor at a hardware level.
Enhancing Productivity with External Monitors
Adding external monitors to your Mac can transform how you work and boost your efficiency. Multiple screens give you more space to organize your tasks and see more information at once.
Optimizing Workflow with Monitor Setup
The way you arrange your monitors matters for productivity. Many Mac users find that a dual monitor setup significantly boosts productivity by providing more screen space.
Try placing your main work on the primary screen and reference materials on the secondary display. This setup works well for tasks like coding, writing, or data analysis.
For video editors and graphic designers, a vertical monitor orientation can help with timeline views and code editing. You can change display orientation in System Settings > Displays.
Consider monitor placement for comfort. Position screens at eye level to avoid neck strain during long work sessions. The main screen should be directly in front of you, with secondary monitors at comfortable viewing angles.
Software Tools and Applications
Several apps help you manage multiple screens on Mac. Rectangle and Magnet let you quickly snap windows to different parts of your screens using keyboard shortcuts.
BetterTouchTool offers custom window management with drag-and-drop features and keyboard shortcuts. It lets you create workflows that move windows between monitors.
For programming work, VS Code and Xcode work well in multi-monitor setups. Keep your code on one screen and documentation or preview windows on another.
Microsoft Office users can spread Excel, Word, and PowerPoint across monitors. View presentation slides on one screen while editing notes on another. This setup works great for preparing class materials or business presentations.
Screen recording software like QuickTime or OBS Studio benefits from multiple monitors. Keep recording controls on one screen while capturing content on another.
Peripheral Devices Integration
External monitors work best when part of a complete setup. A good keyboard and mouse make controlling multiple screens easier. Wireless options reduce cable clutter.
For creative work, connect drawing tablets to your Mac while using external displays for reference materials. The tablet can even serve as an additional input device.
Printers and scanners connect easily to multi-monitor Mac setups. Put printer controls on a secondary screen while keeping your main work uncluttered.
Consider a proper USB-C hub or docking station to connect all your devices. This creates a clean setup where you can plug in your MacBook with a single cable to connect to monitors, peripherals, and power.
Smart TVs can function as extra displays for presentations or media viewing. This works well for meetings where you need to show content to others.
Frequently Asked Questions
Connecting an external monitor to your Mac involves different methods depending on your ports and setup needs. Here are answers to common questions about making these connections work smoothly.
What are the steps to connect an HDMI monitor to a MacBook Air?
Connecting an HDMI monitor to your MacBook Air is straightforward. First, get an HDMI cable that works with both your monitor and MacBook.
If you have a newer MacBook Air with an HDMI port, plug the cable directly into this port. For older models without HDMI ports, you’ll need an adapter that converts from USB-C or Thunderbolt to HDMI.
Once connected, your Mac should detect the monitor automatically. If not, go to System Preferences > Displays to adjust settings.
How can I use a USB-C connection to attach an external display to my MacBook?
USB-C connections offer a simple way to connect external displays to newer MacBooks. Find a USB-C cable that’s compatible with your monitor, or use a USB-C to DisplayPort/HDMI adapter if needed.
Connect one end to your MacBook’s USB-C port and the other to your monitor. Your Mac should recognize the monitor right away.
Many USB-C monitors also provide power to your MacBook through the same cable, eliminating the need for a separate power cord.
What is the process for setting up a wireless connection between a MacBook and an external monitor?
Wireless connections require compatible hardware on both devices. Apple’s AirPlay technology lets you connect to compatible smart TVs or monitors wirelessly.
To use AirPlay, make sure both your Mac and display are on the same Wi-Fi network. Click on the Control Center icon in the menu bar, select Screen Mirroring, and choose your display from the list.
For non-AirPlay displays, third-party adapters like Google Chromecast or specialized wireless HDMI kits can create wireless connections between your Mac and monitor.
How do I configure the display settings to make the external monitor the primary screen on my Mac?
Making your external monitor the primary screen takes just a few clicks. First, connect your monitor to your Mac and ensure it’s detected.
Open System Preferences (or System Settings in newer macOS versions) and select Displays. In the Arrangement tab, you’ll see icons representing your screens.
Drag the white menu bar from your Mac’s built-in display to the external monitor icon. This tells your Mac to use the external display as the primary screen. Your main desktop and menu bar will now appear on the external monitor.
Is there a compatibility list available for monitors that work with Mac computers?
Apple doesn’t publish an official comprehensive list of compatible monitors. Most modern displays will work with Mac computers through the appropriate connections.
For optimal compatibility, monitors designed specifically for Mac often provide better integration and color accuracy. These monitors sometimes advertise “Mac compatibility” or “designed for Mac” on their packaging.
Before purchasing, check the monitor’s specifications to ensure it has connection types that match your Mac’s ports or can be adapted easily.
Can I use a USB adapter to connect my Mac computer to a monitor, and what are the implications for video quality?
Yes, USB adapters can connect Macs to external monitors when direct connections aren’t possible. Various adapters convert from USB-C or Thunderbolt to HDMI, DisplayPort, or VGA.
USB-C adapters generally maintain good video quality, especially those using USB-C to HDMI or DisplayPort. For highest quality, choose adapters that support the resolution and refresh rate of your monitor.
Cheaper adapters might cause reduced resolution, frame rate limitations, or color accuracy issues. For professional work requiring precise colors or high resolutions, investing in a quality adapter or direct connection is recommended.