NVIDIA’s highly anticipated Blackwell AI chips are facing significant delays due to design flaws. These setbacks may postpone their launch until 2025, affecting major clients such as Microsoft and Google. In a surprising turn of events for the company, the upcoming Blackwell AI chips have encountered a major roadblock because of a late-stage design flaw.
This delay has far-reaching implications for NVIDIA, its customers, and the broader AI industry. This article explores the causes of the delay, potential solutions, and the ripple effects it could have on the competitive landscape of AI chip development.
Short Summary:
- NVIDIA’s Blackwell AI chip launch may be delayed for more than three months due to design flaws.
- Major clients such as Meta, Google, and Microsoft are expected to be affected.
- The delay is linked to production issues at TSMC, requiring a redesign of the chip.
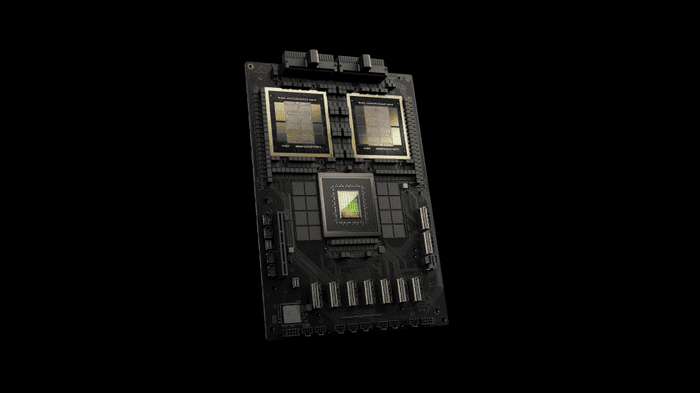
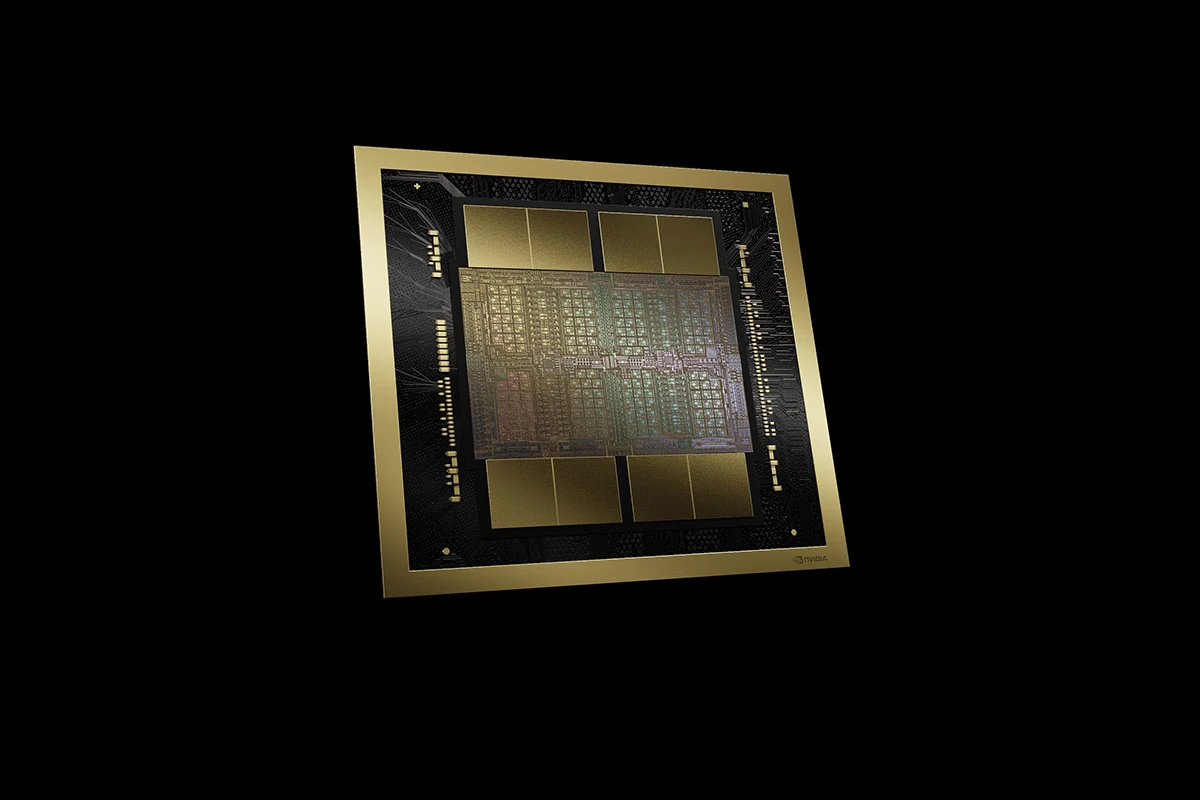
NVIDIA’s highly anticipated Blackwell GPUs for artificial intelligence workloads are facing a delay of at least three months due to a design flaw in the processor die connecting two Blackwell GPUs on a single NVIDIA Superchip. The delay is a result of production issues with NVIDIA’s upcoming chips from the Blackwell series. According to reliable insider information from The Information, the launch is now expected to be postponed by three months or more due to design complications.
The setback is especially concerning for major clients, including tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Meta, which have placed substantial orders for NVIDIA’s latest AI innovations. The issue appears to stem from a design flaw related to the processor die responsible for connecting two Blackwell GPUs, as reported by sources involved in chip and server hardware production. This defect was initially discovered during production at Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), leading to a redesign and preventing mass production from commencing as initially planned.
Navigating Roadblocks: NVIDIA’s Blackwell Chip Delay
Impact on Customers and Competitors
The delay affects major clients like Microsoft, Meta, and Google, who rely on NVIDIA’s technology for their AI initiatives. It also gives competitors like Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) an opportunity to gain ground in the market with their upcoming AI chip releases.
Cause of the Delay
The design flaw, discovered by one of NVIDIA’s key manufacturing partners, TSMC, necessitates a redesign of the chip. This requires a new production test before mass production can resume, pushing back the expected launch date to the first quarter of 2025.
Possible Solutions
To mitigate the delay, NVIDIA is exploring several options:
- Redesigning the Chip: This is the primary solution, but it requires time and resources to complete.
- Producing a Single-GPU Version: This could be a quicker fix, but it may sacrifice performance.
- Prioritizing Certain Models: NVIDIA could prioritize the production of less complex models to expedite delivery to customers.
Financial Implications
The delay is expected to impact NVIDIA’s financials, with lower-than-anticipated supply of Blackwell chips in Q4 2024 and H1 2025. This could affect revenue and market share, especially as competitors release their AI chips.
Potential Impact of Delay
| Stakeholder | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| NVIDIA | Lower revenue, reduced market share, potential loss of customer trust |
| Microsoft, Meta, Google | Delayed AI projects, potential increased costs |
| AMD | Opportunity to gain market share, increased investor interest |
| TSMC | Temporary idle production lines, potential loss of revenue |
“The production is on track to ramp later this year,” stated an NVIDIA spokesperson, who refrained from confirming links to the reported delays and urged caution regarding proceedings. — The Information

NVIDIA had aimed for an aggressive rollout, hoping to ship the Blackwell chips by the end of 2024. However, indications now suggest that major shipments may not occur until the first quarter of 2025. Microsoft, one of the primary customers, has already been notified about these delays affecting its most advanced models from the Blackwell series.
In the meantime, the supply chain shortage is exacerbated by the transition at TSMC from CoWoS-S to CoWoS-L technology, which is essential for the production of NVIDIA’s advanced chips. According to SemiAnalysis’s Dylan Patel, the supply of Blackwell chips is poised to be considerably lower than anticipated for the latter part of 2024 and the first half of 2025 as TSMC works through these backing technology changes.
Major Clients Impacted
With significant orders in place, the delays are likely to strain NVIDIA’s relationships with its major clients, including:
- Meta Platforms
- Microsoft Corporation
- Google LLC
- Amazon Web Services
The direct impact on these firms arises not only from halted production but also from their operational reliance on NVIDIA’s advanced AI capabilities to power applications and services that demand immense computational strength. NVIDIA’s Blackwell chips are designed to offer groundbreaking processing capabilities, pushing the limits of what’s possible in machine learning and artificial intelligence systems.
“Delays like this can significantly affect strategic roadmaps for companies looking to deploy advanced AI applications,” remarked an industry analyst who requested to remain anonymous.
Technical Challenges and Solutions
The design flaws informing these delays relate specifically to the improvement of the Blackwell architecture’s interconnect technology. These components are critical for efficient communication between the GPUs and memory systems, and resolution of the issues discovered will necessitate a redesign of specific die bridge elements. Additionally, the technology requires rigorous validation and testing before it can enter mass production.
As NVIDIA navigates through these challenges, speculation arises regarding the potential for a single-GPU version of the Blackwell chip to expedite delivery timelines. This pivot could enable NVIDIA to supplement its current product line while addressing immediate demand from its clients.
Production Dynamics with TSMC
The relationship between NVIDIA and TSMC is more critical than ever as the latter combats production inefficiencies during a pivotal time of transformation in chip-making technology. Current conditions at TSMC’s rollout of CoWoS-L technology could stifle production capacity, leaving NVIDIA with an uphill battle to meet its delivery commitments.
Industry insiders have suggested that as TSMC upgrades its facilities—specifically the AP6 site dedicated to new CoWoS-L capacity—NVIDIA may face substandard output until these systems are fully operational. An anonymous source associated with chip design therein expressed concern regarding the ability to fulfill the volumes initially anticipated.
“Limited capacity and ongoing transitions will hinder the ramp-up of production, which is essential for NVIDIA,” said a TSMC representative who did not wish to disclose their name.
NVIDIA’s Strategic Position Moving Forward
As NVIDIA grapples with these technical and logistical impediments, their strategy will likely encompass not only the resolution of Blackwell’s design issues but also an enhancement of their supply chain adaptability. Increasing reliance on alternative product lines such as Hopper may be crucial for maintaining client satisfaction in the short term.
According to sources, NVIDIA is expected to prioritize the production of GB200 NVL72 units over the NVL36 variants. The NVL72 design incorporates 72 GPUs compared to the NVL36’s 36, allowing for significantly more computational power concentrated in a single hardware rack. This upswing in focus on NVL72 could help mitigate anticipated losses in revenue and production resulting from Blackwell’s challenges.
What Lies Ahead for Competitors
Amidst NVIDIA’s struggles, competitors like AMD and Intel are on the brink of launching their own AI chip offerings. Intel’s Falcon Shores will be hitting the market in the next year, and AMD’s Instinct MI400 is slated for a 2026 release. The unfolding scenario adds pressure on NVIDIA to expedite resolution of existing problems if they hope to stay ahead in the highly competitive AI chip market.
“The delay of Blackwell gives rivals an opportunity to close the gap, which NVIDIA must counter swiftly,” stated an analyst from a prominent tech research firm.
Long-Term Implications for AI Development
The postponement of Blackwell heralds broader implications for the progression of AI technologies globally. As tech enterprises secure resources and infrastructure capable of leveraging advanced AI capabilities, unmet timelines risk creating delays in innovation across multiple sectors.
Market analysts speculate that continued reliance on NVIDIA’s older architectures, such as Hopper, may suffice for immediate demands but further limitations will emerge as the desire for cutting-edge performance escalates.
Until further information is released by NVIDIA, stakeholders will be closely monitoring the situation to gauge the potential cascade of effects this delay could initiate throughout the tech ecosystem.