Nintendo has confirmed that Switch 2 Joy-Con controllers will not use Hall Effect sticks, disappointing many fans who hoped for this drift-resistant technology. The decision comes despite the controllers being fully redesigned for the upcoming console. Nintendo explained that Hall Effect joysticks can’t be used with the Switch 2 because they would interfere with the powerful magnets that keep the Joy-Cons attached to the system.
While this news may worry gamers who struggled with stick drift on the original Switch, Nintendo has promised that the new Joy-Con design “feels really good” despite not using Hall Effect sensors. The company has likely made other improvements to address the drift issues that plagued the original controllers. Many fans speculate that Nintendo’s decision may also be related to patent costs for the technology.
Nintendo Switch 2 Joy-Con Controllers Will Not Feature Hall Effect Joysticks
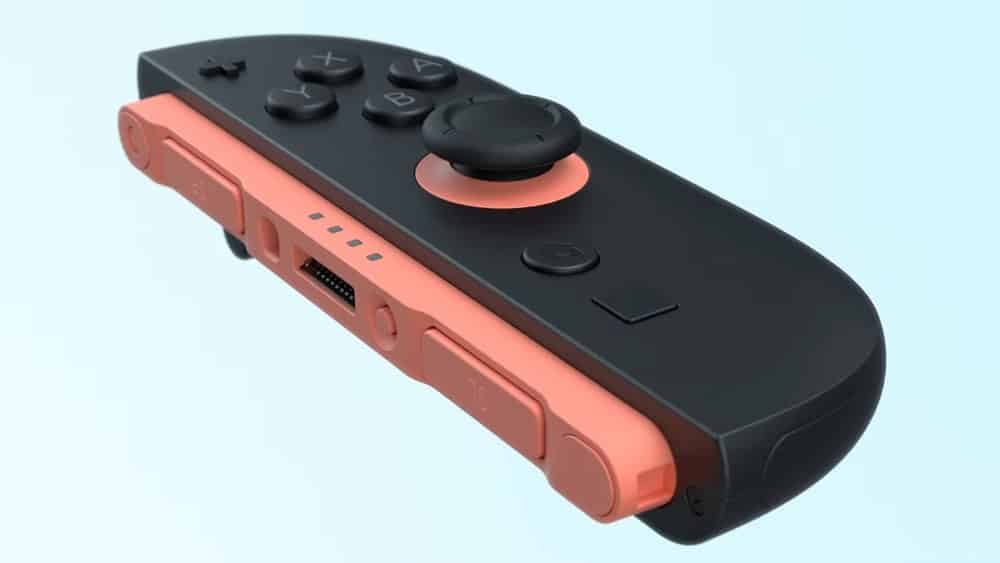

Nintendo has officially confirmed that the Joy-Con controllers for the upcoming Nintendo Switch 2 will not incorporate Hall effect joysticks—a technology known for its resistance to stick drift. This decision has sparked discussions among gamers, especially considering the drift issues that plagued the original Switch’s Joy-Cons.
Understanding the Decision
In an interview, Nintendo of America’s Nate Bihldorff stated that while the new Joy-Con controllers have been redesigned from the ground up, they do not utilize Hall effect sticks. He emphasized that despite this, the controllers “feel really good”. Additionally, Switch 2 producer Kouichi Kawamoto mentioned that the control sticks are larger, more durable, and offer smoother movement compared to their predecessors.
Alternative Technologies and Considerations
While Hall effect sensors are effective in preventing stick drift by eliminating physical contact points, they are not without drawbacks. Some users have noted that Hall effect sticks can be sensitive to external magnetic fields and temperature changes, potentially affecting performance. There’s also speculation that Nintendo might be exploring other technologies, such as Tunneling Magnetoresistance (TMR) sensors, which offer similar benefits without some of the limitations associated with Hall effect sensors.
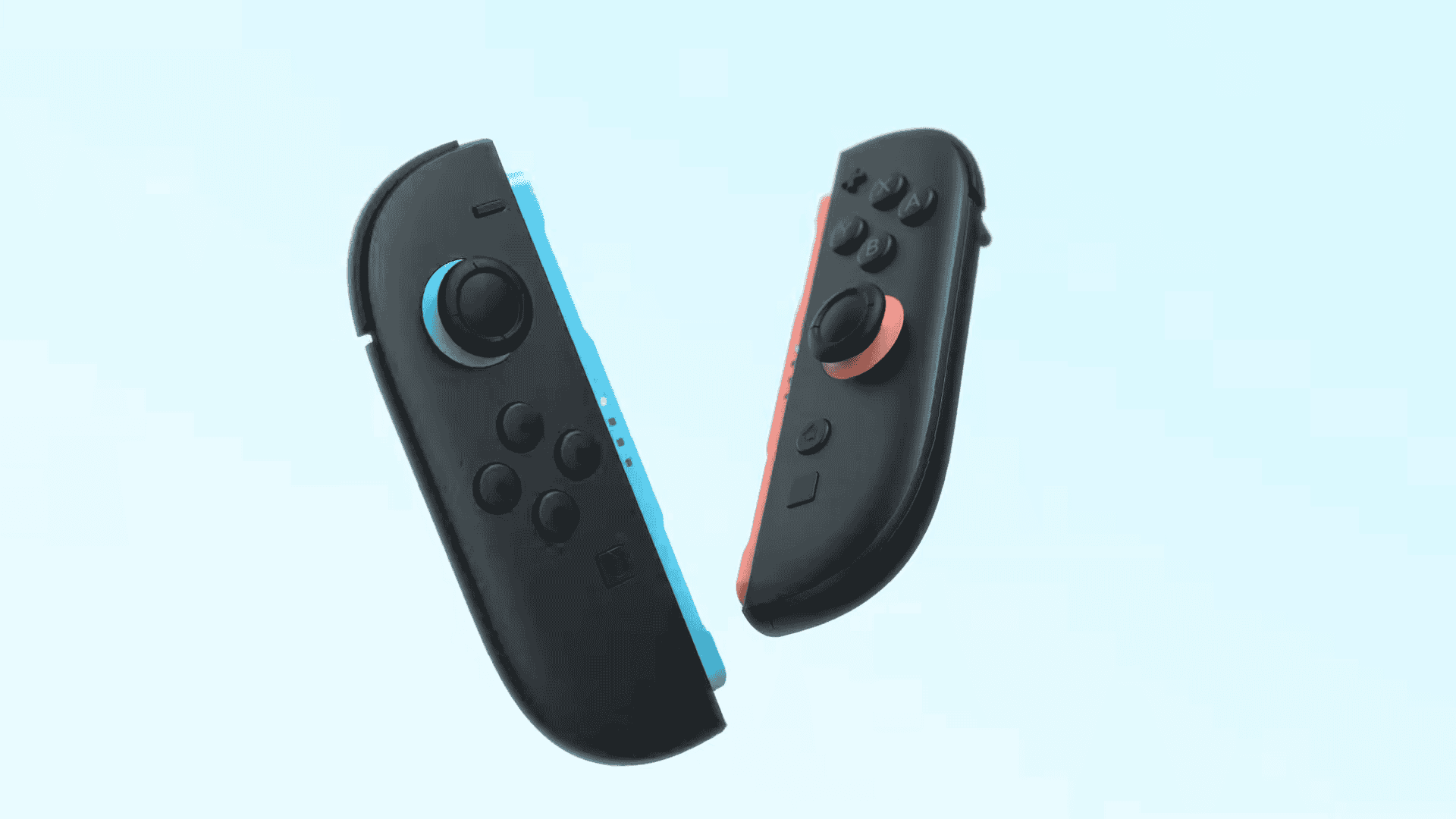

Community Reactions
The gaming community has expressed mixed feelings about this decision. Some users are disappointed, citing the persistent drift issues with the original Joy-Cons. Others are more optimistic, hoping that Nintendo’s redesign will address these concerns effectively. Discussions have also touched on the potential use of alternative technologies like TMR sensors, which could offer a balance between performance and durability.
Comparative Overview
Here’s a comparison between traditional potentiometer-based joysticks, Hall effect sensors, and TMR sensors:
| Feature | Potentiometer-Based | Hall Effect Sensors | TMR Sensors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drift Resistance | Low | High | High |
| Sensitivity to Fields | Low | High | Moderate |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate | Low | High |
| Cost | Low | High | Moderate |
| Adoption in Industry | High | Growing | Emerging |
Note: The above table is based on general industry observations and may vary depending on specific implementations.
Looking Ahead
While the absence of Hall effect sensors in the Switch 2’s Joy-Cons might be seen as a missed opportunity by some, it’s important to consider that Nintendo has focused on enhancing the overall design and durability of the controllers. The true test will come post-launch, as users experience the new controllers firsthand and provide feedback on their performance and longevity.
Key Takeaways
- Switch 2 Joy-Con controllers cannot use Hall Effect sticks because of magnetic interference with the attachment system.
- Nintendo has redesigned the controllers with alternative improvements to address the previous drift issues.
- The new Joy-Con design prioritizes the magnetic attachment mechanism while seeking other solutions for stick durability.
Evolution of Switch Controllers
Nintendo’s controllers have changed a lot since the original Switch launched. The company has made important design choices that affect how players interact with their games.
From Original Joy-Con to Joy-Con 2
The original Joy-Con controllers suffered from a major problem: stick drift. This issue caused characters to move in games even when players weren’t touching the sticks.
Nintendo faced several lawsuits because of this problem. Many players had to send their controllers for repairs or buy new ones.
The new Joy-Con 2 controllers for Switch 2 have been fully redesigned. Nintendo of America spokesperson Nate Bihldorff confirmed they don’t use Hall effect sensors. Still, he claims “they feel really good.”
One possible reason for avoiding Hall effect joysticks is the magnetic connection. The Joy-Cons use powerful magnets to attach to the system, which could interfere with magnetic sensors.
Comparing Switch 2 Joy-Con and Pro Controller
The Switch Pro Controller has always been more durable than the Joy-Cons. Many serious gamers prefer it for longer gaming sessions.
The Switch 2 Pro Controller might use different technology than the Joy-Cons. Nintendo hasn’t confirmed if it will use Hall effect sticks, which would make it more reliable.
Key differences between Joy-Con 2 and the Pro Controller include:
- Size: Pro Controller is larger with a traditional design
- Battery life: Pro typically lasts longer between charges
- Button layout: Pro has a more standard arrangement
- Durability: Pro tends to be more robust
Nintendo has been quiet about exactly what improvements they’ve made to prevent stick drift in the Switch 2 controllers.
Industry Standards: PC, Xbox, and PlayStation
Other gaming platforms have moved ahead with stick technology. Many third-party controllers for PC, Xbox, and PlayStation now use Hall effect joysticks.
These magnetic sensors don’t wear out like traditional joysticks. This means they avoid stick drift almost entirely.
Steam Deck and other handheld PC gaming devices come with Hall effect sticks. This shows Nintendo is falling behind industry standards.
Xbox controllers have faced drift issues too, but Microsoft has worked to improve them. PlayStation’s DualSense controller uses different technology but still faces some drift problems.
Players can often replace sticks on third-party controllers, something not possible with Joy-Cons. This repairability is becoming an important factor for many gamers.
Technical Insights into Hall Effect Technology
Hall Effect technology offers a promising solution to the persistent joy-con drift issues that have plagued Nintendo controllers. This magnetic sensing approach works differently from traditional analog sticks and provides several advantages in durability and performance.
Understanding Hall Effect Sensors
Hall Effect sensors detect magnetic fields to measure movement in joysticks. Unlike traditional analog sticks that use physical contact between components, Hall Effect sticks rely on magnets and sensors that never touch. This lack of physical contact is key to their durability.
The technology works by placing a small magnet near a semiconductor material. When the joystick moves, the magnet shifts position. This movement changes the magnetic field around the semiconductor, creating a measurable voltage change called the “Hall Effect.”
These sensors track stick position with great accuracy without mechanical wear. Since there’s no rubbing of parts against each other, the sensors don’t develop the worn-down areas that cause drift in standard controllers.
Design Considerations and Advancements
Implementing Hall Effect sticks requires careful design planning. One challenge involves powerful magnets used to attach joy-cons to the console. These magnets could interfere with the Hall sensors’ magnetic field detection.
Modern Hall Effect sticks use advanced calibration software to maintain accuracy over time. This software helps correct minor deviations that might occur from temperature changes or aging.
The sticks also feature improved power efficiency compared to older models. This matters for portable systems like the Switch where battery life is important.
Manufacturers have developed Hall Effect sticks in various sizes to fit different controller designs. Some versions include added features like pressure sensitivity for more gameplay options.
Addressing Stick Drift with Hall Effect Sticks
Stick drift occurs when controllers register movement without user input. Traditional joy-cons develop drift when graphite pads wear down from repeated contact with metal sensors.
Hall Effect technology could fix this issue by eliminating contact points that wear out. Without physical friction between parts, these sticks maintain their accuracy much longer.
Third-party controllers with Hall Effect sticks have shown promising results in fighting joy-con drift. Many users report these controllers working perfectly even after months or years of heavy use.
While no technology is perfect, Hall Effect sticks have a much lower failure rate than traditional analog sticks. The main trade-offs are slightly higher manufacturing costs and design complexities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Nintendo Switch 2 owners often face controller issues that can affect gameplay. These common problems include drift, connectivity issues, and calibration errors that may require specific solutions.
What are the common causes for Joy-Con controller malfunctions on the Nintendo Switch 2?
Joy-Con malfunctions on the Switch 2 may happen due to dust build-up under the joystick. This is especially true since Nintendo won’t be using Hall Effect sticks in the new controllers.
Physical damage from drops or rough handling can also cause buttons to stick or not respond. Sometimes the issue stems from low battery levels affecting performance.
Interference from other electronic devices may disrupt the Bluetooth connection. The magnetic attachment system can sometimes create problems with alignment and connectivity.
How can one troubleshoot connectivity issues with Switch 2 Joy-Con controllers?
First, try restarting the console by holding the power button for three seconds. This simple step often fixes minor connection problems.
Make sure the Joy-Con controllers are fully charged. Low battery can cause intermittent connectivity issues.
Update the controller firmware through the System Settings menu. Nintendo regularly releases fixes for known issues.
Remove other Bluetooth devices from the area to reduce interference. This includes phones, tablets, and wireless headphones.
Try re-pairing the controllers by attaching them to the console and then detaching them. This resets the connection.
What steps should be taken to resolve drifting issues in Joy-Con controllers without Hall Effect sticks?
Clean under the joystick caps using compressed air or electronic contact cleaner. Since the Switch 2 won’t have Hall Effect sticks, regular cleaning is important.
Calibrate the controllers through the System Settings menu. This can sometimes fix minor drift issues.
Allow the controller to fully discharge, then recharge it completely. This can reset internal components.
If the problem persists, consider using the calibration tool in settings. It helps adjust the center position of the joysticks.
For severe cases, contact Nintendo support as the issue might require professional repair.
Are there any official repair services offered by Nintendo for faulty Joy-Con controllers?
Nintendo offers a standard warranty service for all Switch 2 controllers. This typically covers manufacturing defects for 12 months from purchase.
Even outside warranty, Nintendo has been known to repair Joy-Con drift issues at reduced or no cost in many regions.
To use the service, visit Nintendo’s support website and fill out a repair request form. You’ll receive shipping instructions and an estimate.
Turnaround time is usually 1-2 weeks depending on your location. Nintendo sometimes extends repair programs for known issues.
How can users properly calibrate Switch 2 Joy-Con controllers to ensure accurate control?
Access calibration through System Settings > Controllers and Sensors > Calibrate Control Sticks. Follow the on-screen instructions carefully.
For best results, place the console on a flat surface during calibration. Avoid moving the controllers except when prompted.
After calibration, test in a game with precise controls to confirm improvement. If issues persist, try the calibration process again.
Nintendo’s official support site offers video tutorials for proper calibration. These can be helpful for first-time users.
What are the recommended ways to maintain the longevity of Joy-Con controllers for the Switch 2?
Clean the controllers regularly with a soft, dry cloth. Pay special attention to the joystick areas where dust collects.
Store controllers in a case when not in use. This prevents dust build-up and protects them from accidental damage.
Avoid eating while playing to prevent crumbs and sticky substances from getting into the controls.
Update controller firmware whenever prompted. These updates often include improvements to stability and performance.
Don’t leave controllers in extremely hot or cold environments. Temperature extremes can damage internal components and battery life.