Alphabet, the parent company of Google, is emerging as a serious competitor in the AI hardware market and is poised to challenge NVIDIA’s long-standing dominance with its Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). As AI adoption accelerates across various industries, the demand for advanced hardware solutions is increasing, putting Alphabet in a strong position to compete in this high-stakes environment.
To fully leverage this opportunity, Alphabet should focus on improving its strategy by prioritizing developer engagement, enhancing the accessibility of its technology, and streamlining organizational efforts. These steps will be essential for expanding the influence of its TPUs and establishing a foothold in the rapidly growing AI chip market, which is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
The competition between Alphabet and NVIDIA extends beyond just hardware performance; it also involves creating robust AI ecosystems that seamlessly integrate hardware and software to attract developers and businesses. With TPUs that offer scalable solutions tailored for AI workloads, Alphabet has the potential to disrupt NVIDIA’s leadership in the industry and reshape the future of AI hardware innovation.
The AI Hardware Race: Alphabet and Nvidia Compete

Alphabet’s AI Push
Alphabet, Google’s parent company, is making big moves in artificial intelligence. They’re not just building software; they’re developing the hardware that powers AI too. This puts them in direct competition with Nvidia, the current leader in AI chips. Alphabet’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) are specialized chips designed for machine learning tasks. These chips are used in Google’s data centers to power services like Search, YouTube, and Translate. Alphabet is investing heavily in these TPUs, improving their performance with each new generation. This investment shows their commitment to becoming a major player in the AI hardware market.
Nvidia’s Dominance and Challenges
Nvidia’s Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) have become the standard for AI workloads. Their GPUs offer parallel processing power, which is ideal for the complex calculations involved in machine learning. This has made Nvidia a dominant force in the AI hardware market. However, Nvidia faces challenges. As AI models grow larger and more complex, the demand for even more powerful hardware increases. This opens the door for competitors like Alphabet to offer alternative solutions. The company’s stock price has fluctuated in recent times due to the changing market dynamics. It’s important to note that Nvidia’s market capitalization is still substantial, at around $1 trillion, dwarfing most competitors.
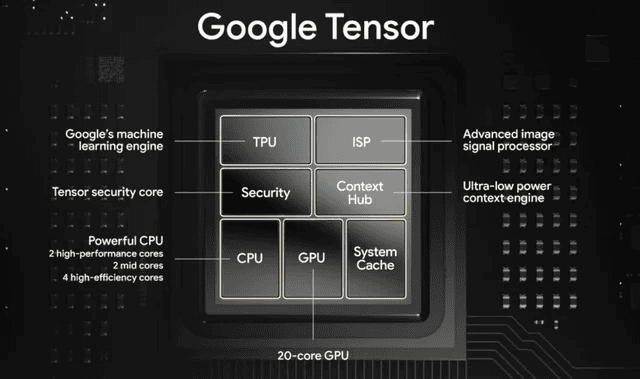
Comparing TPUs and GPUs
Both TPUs and GPUs are designed for AI, but they have different strengths. GPUs are more general-purpose, meaning they can handle a wider range of tasks. TPUs are more specialized, optimized specifically for machine learning. This specialization can make TPUs more efficient for certain AI workloads. However, the wider availability and established software ecosystem around GPUs give Nvidia an edge. For example, Nvidia’s CUDA platform is widely used by AI developers. This makes it easier for them to develop and deploy AI applications on Nvidia hardware. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | TPU | GPU |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization | Optimized for machine learning | General-purpose, good for many tasks |
| Efficiency | Can be more efficient for specific AI tasks | Good all-around performance |
| Software Ecosystem | Growing, but less mature than GPUs | Mature, with strong developer support (CUDA) |
| Availability | Primarily used within Google’s infrastructure and cloud services | Widely available from many vendors |
The Impact of AI on the Market
The rise of AI is creating a huge demand for specialized hardware. This is driving innovation and competition in the chip industry. Companies like Alphabet and Nvidia are investing billions of dollars in research and development to create more powerful and efficient AI chips. This competition is good for consumers, as it leads to better technology and potentially lower prices. The market for AI chips is predicted to continue to grow rapidly in the coming years. Some analysts predict the market will reach hundreds of billions of dollars in the next few years. This growth is driven by the increasing use of AI in various industries, from healthcare to finance.
The Cloud Computing Angle
Cloud computing plays a key role in the AI hardware race. Both Alphabet and Nvidia offer cloud-based AI services. Google Cloud offers access to TPUs, while Nvidia offers GPUs through various cloud providers. This allows businesses to use powerful AI hardware without having to invest in their own infrastructure. This is especially important for smaller businesses and startups that may not have the resources to buy and maintain their own hardware. The cloud also enables scalability, allowing businesses to easily increase or decrease their computing power as needed.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AI Hardware
The future of AI hardware is likely to involve even more specialized chips designed for specific AI tasks. We may also see the rise of new types of hardware architectures that are even more efficient for machine learning. Quantum computing is another area of research that could have a big impact on AI in the future. While still in its early stages, quantum computing has the potential to solve certain types of problems that are impossible for today’s computers. This could lead to breakthroughs in AI and other fields.
The Software Side of AI
While hardware is essential, software is just as important in the AI ecosystem. Frameworks like TensorFlow (developed by Google) and PyTorch are widely used for developing AI models. These frameworks provide tools and libraries that make it easier for developers to build and train AI systems. The software ecosystem around these frameworks is constantly evolving, with new tools and techniques being developed all the time. This software development is crucial for making the most of the available hardware.
The competition between Alphabet and Nvidia is not just about hardware. It’s also about building a complete AI ecosystem that includes both hardware and software. This ecosystem includes everything from the chips themselves to the software tools that developers use to build AI applications. The company that can build the most compelling ecosystem is likely to be the leader in the AI race. This competition will continue to drive innovation and shape the future of artificial intelligence.
Short Summary:
- Alphabet’s tensor processing units are seen as a strong alternative to Nvidia’s GPUs.
- Analyst Gil Luria highlights that Alphabet is underutilizing its AI hardware market potential.
- A combination of Alphabet’s TPU and DeepMind businesses could be valued at $700 billion.
As we navigate through a rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence and machine learning, Alphabet Inc. (NASDAQ: GOOGL) is quietly positioning itself as a significant player with the potential to challenge established titans like Nvidia (NASDAQ: NVDA). According to D.A. Davidson analyst Gil Luria, Alphabet’s tensor processing units (TPUs) represent a compelling alternative to Nvidia’s popular graphics processing units (GPUs). In a recent note, Luria emphasized that these TPUs are not just viable alternatives but could be even superior, citing Apple’s recent decision to utilize TPUs for model training as supporting evidence.
“Alphabet has the most compelling alternative to Nvidia GPUs,” —Gil Luria, D.A. Davidson analyst.
Despite the promising potential of Alphabet’s AI chip business, Luria offers a more reserved perspective on the company’s forward momentum. His neutral rating on Alphabet reflects concerns about the organization’s strategy in an expansive estimated $4 trillion market for AI hardware. He notes that “Alphabet does not appear to be aggressive enough pursuing this opportunity,” and suggests that the company has “historically made it difficult for external developers to access and effectively utilize TPUs,” increasing operational bottlenecks.
In comparison, Luria points out that Nvidia boasts a highly robust ecosystem for developers, making its GPUs significantly more accessible compared to Alphabet’s offerings. This competitive edge has fueled Nvidia’s recent growth and dominance in the AI hardware market.
Luria’s insights extend beyond immediate concerns; he raises the possibility of a sum-of-the-parts valuation for Alphabet that could reveal substantial hidden value within the company. He estimates a combined value of $700 billion for their TPU and Google DeepMind businesses, suggesting that the previously underappreciated divisions are pivotal to Alphabet’s future.
“The combination of Alphabet’s TPU business and its Google DeepMind AI business could be worth $700 billion.”
To put this in context, the valuations of rivals such as Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) and Nvidia significantly frame the conversation. AMD, without an equivalent to DeepMind, is currently worth about $200 billion, while Nvidia’s staggering market cap stands at approximately $3.5 trillion. These figures underline the potential that Alphabet may have, provided it capitalizes on its existing technology and strategic positioning.
Luria’s analysis also features a broader valuation for Alphabet, estimating the company could be valued at $3.5 trillion. He attributes a value of $300 billion to YouTube, close to $700 billion for Google Cloud, and $1.3 trillion for the search and networking segments. However, Luria cautions that the company’s value cannot be fully realized unless it indicates a willingness to “release some of the SOTP value to shareholders,” pressing on a dual opportunity for growth and organizational introspection.
Market Dynamics and Future Prospects
As the artificial intelligence space continues to evolve and mature, Alphabet’s role within it remains pivotal. The competition with established firms like Nvidia poses significant challenges, yet the potential for Alphabet’s TPU technology to reshape the hardware landscape cannot be overlooked. Alphabet’s ability to navigate complexities surrounding chip accessibility and the developer ecosystem will ultimately dictate the trajectory of its market presence.
The burgeoning market for AI technology, which is expected to balloon to $4 trillion, presents an increasingly attractive landscape ripe for innovation and expansion.
“We are waiting for the company to indicate it is willing to release some of the SOTP value to shareholders.”
—Gil Luria
As more enterprises recognize the capabilities offered by AI hardware, firms like Alphabet must adapt and evolve. Their approach to streamlining access to TPUs could be a game-changer, offering a competitive edge at a crucial juncture. Alphabet may need to adopt a more aggressive positioning strategy and collaborate with developers to fully harness their technological assets.
Moreover, the potential for an internal shift or even a breakup of segments within Alphabet could assist in realizing value more comprehensively. Such a transformation could pave the way for each segment to be valued according to its specific market potential, further fueling Alphabet’s growth ambitions.
Additionally, in light of these competitive pressures, Alphabet’s management strategy may require a reassessment. The company’s adaptive ability might be tested by new entrants and innovations in the AI hardware sector, which are rapidly evolving. Collaborations or strategic partnerships to amplify the reach and utility of Alphabet’s technologies could be vital in ensuring sustained momentum.
Towards a Greater Market Share
Investors and analysts alike are closely monitoring Alphabet’s moves in the artificial intelligence space. The organization’s strategies could lead to a substantial uptick in engagement within a space that is swiftly becoming the centerpiece of technological advancement. Analysts predict that should Alphabet amplify its focus on contemporary market needs and ramp up collaboration, a shift toward a more progressive structure could unfold, capturing a significant share of the lucrative AI market.
The bottom line is that Alphabet’s powerful AI chip business, characterized by its high-performance TPUs, coupled with innovative ventures such as Google DeepMind, creates a fertile ground for opportunity. However, to effectively compete with Nvidia’s established status, Alphabet must initiate proactive measures to broaden developer access and enhance the commercial viability of its hardware. These steps will be critical in determining whether Alphabet can redefine its position within the AI ecosystem.







