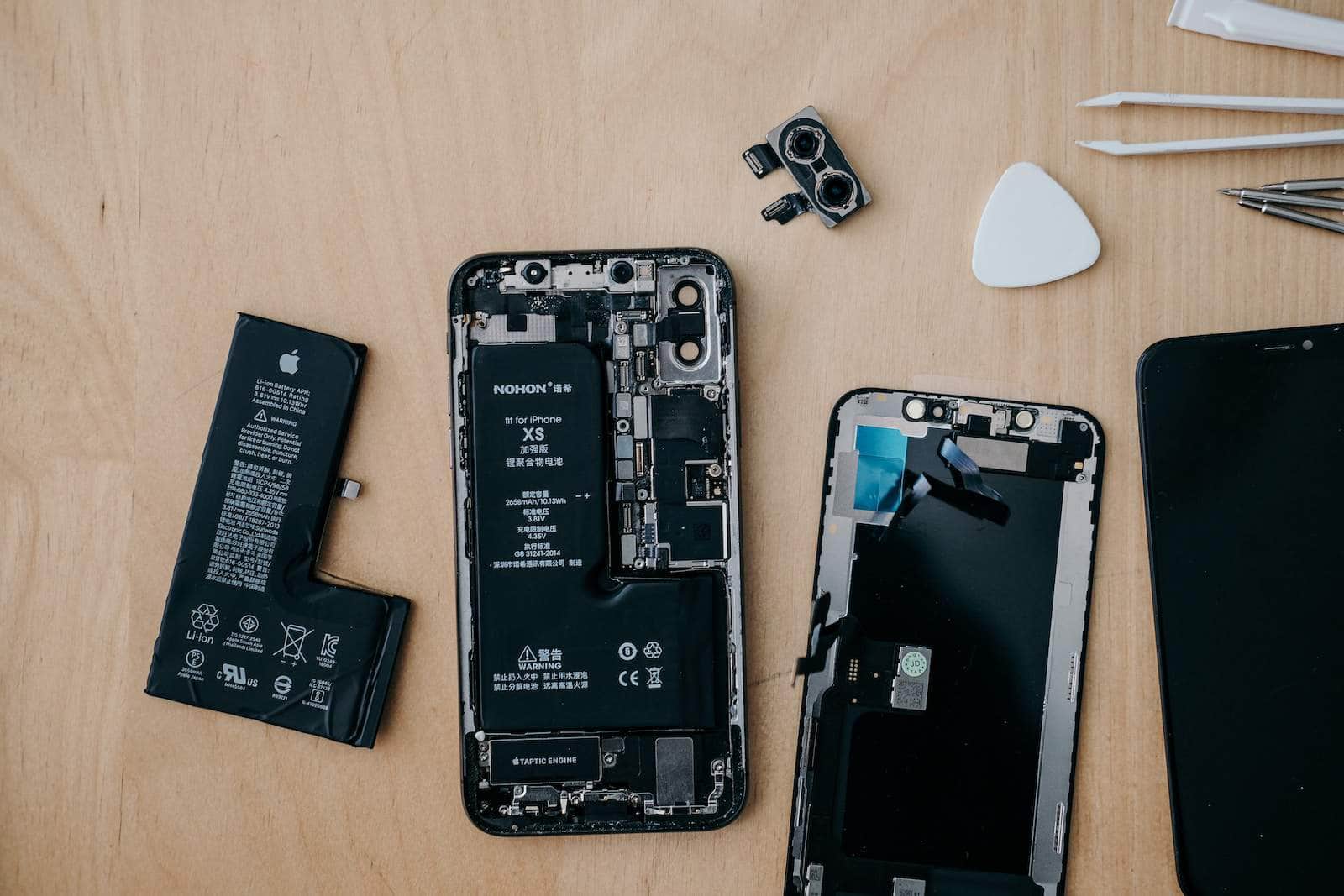
All cell phones are unique electronic devices, but most of the “guts” on the inside share common functions & purposes. This article will go over all the general and specific hardware components you would expect to see when taking apart a phone and will introduce you to the internal “anatomy” of the device.

What’s Inside Your Smartphone?
A Tiny Computer in Your Pocket
Your cell phone is a marvel of modern engineering, packing a ton of technology into a small package. Think of it as a mini-computer you can carry anywhere.
Key Components
Every smartphone has these essential parts:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): This is the brain of your phone, handling all the calculations and tasks. It’s like your phone’s own little thinking cap.
- Memory: This stores your apps, photos, music, and other data. There are two main types: RAM (for short-term storage) and internal storage (for long-term storage).
- Battery: This powers your phone, so you can make calls, browse the web, and play games.
- Screen: This displays all the information you need, from your favorite apps to your latest selfies. Touchscreens even let you control your phone with your finger.
- Camera: This lets you capture photos and videos, so you can share your experiences with friends and family. Some phones even have multiple cameras for different shots.
- Sensors: These tiny components track things like your phone’s movement, orientation, and proximity to your face. They help your phone do all sorts of cool things, like automatically adjust the screen brightness.
Other Important Parts
Your phone also has a bunch of other important bits and pieces, like:
- Modem: This connects your phone to cellular networks, so you can make calls and use data.
- Speakers and Microphones: These let you hear and be heard during calls and when playing media.
- Buttons and Ports: These are used for things like turning your phone on and off, adjusting the volume, and plugging in headphones or a charger.

Components You’ll Find In Every Cell Phone
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Processor | The brain of the phone, responsible for running all the apps and processes. |
| RAM | Temporary storage for data that the phone is currently using. |
| Storage | Permanent storage for apps, photos, videos, and other files. |
| Display | The screen you use to interact with the phone. |
| Battery | The power source that keeps the phone running. |
| Operating System | The software that controls the phone’s basic functions. |
| Camera | Used for taking photos and videos. |
| Microphone | Used for making and receiving phone calls. |
| Speaker | Used for listening to music and other audio. |
| Cellular Antenna | Used for connecting to the cellular network. |
| Wi-Fi Antenna | Used for connecting to Wi-Fi networks. |
| Bluetooth Antenna | Used for connecting to Bluetooth devices. |
| GPS Antenna | Used for location services. |
| Buttons | Used for interacting with the phone, such as the power button and volume buttons. |
| Ports | Used for charging the phone and connecting to other devices, such as the headphone jack and USB port. |
These are just the essential components that every cell phone has. Some phones may have additional components, such as a fingerprint sensor, an iris scanner, or a barometer.
Key Takeaways:
- Processor Complexity: Delve into the intricate System on a Chip (SoC) powering modern smartphones.
- Display Technology: Discover the advanced AMOLED and LCD screens providing vivid visuals.
- RF Innovations: Explore the multi-band RF sections enabling global communication.
- Power Efficiency: Learn about the power management systems that keep our phones running efficiently.
- Versatile Peripherals: Uncover the variety of peripherals, from cameras to sensors, enhancing our user experience.

The Heart of the Smartphone: The Processor
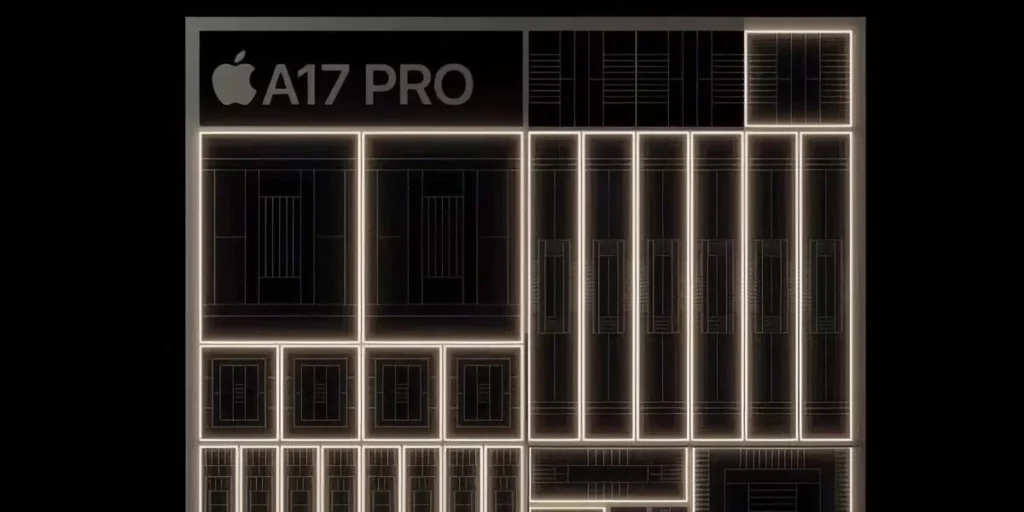
At the core of your smartphone’s hardware lies the system processor. Predominantly, this is a System on a Chip (SoC) which is not just a CPU. It integrates the GPU, LTE modem, and various other processors, making it the most complex component in your phone. For example, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 855, used in phones like the Samsung Galaxy S10, exemplifies this complexity with its multiple CPU cores and advanced graphics processing unit.
The Window to the Digital World: The Display

A smartphone’s display, often an AMOLED or LCD panel, is its most noticeable feature. These displays offer high contrast ratios, fast refresh rates, and wide viewing angles in a thin package. The display subsystem includes the touchscreen interface, significantly offloading the low-level display tasks from the processor.
Global Connectivity: The RF Section
Smartphones must support a wide range of cellular standards, from the latest to older ones like GSM/EDGE. This capability is largely due to a multi-standard modem integrated into the SoC. The RF section also includes sophisticated components for band tuning and signal transmission and reception, ensuring global connectivity.
Maintaining the Power: The Power Management System
Powering a smartphone efficiently is crucial. This involves multiple voltage regulators to manage the varying requirements of different sub-systems. Smartphones typically use li-ion batteries, which require special charging methods and protection against overcharging or short circuits.
The Extended Senses: Peripherals
Smartphones are equipped with various peripherals such as cameras, microphones, speakers, and sensors like accelerometers. Most of these are connected to the mainboard through flexible PCBs, contributing to the phone’s range of functionalities.
Complex Engineering: Putting It All Together
Assembling a smartphone involves integrating a densely packed mainboard, custom-designed batteries, and a rigid metal frame for structural integrity. This complex process ensures that the phone is durable and efficient in its performance.
Ensuring Excellence: Testing and Certifications
Before release, smartphones undergo rigorous testing for safety, performance, and reliability. This includes battery safety tests, Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) evaluations, and performance testing of individual components like the display and camera.
AI Rendering Of A Cellphone’s Hardware
Here’s an AI rendering from Dall-E 3 of the internal hardware of a cell phone. It’s not accurate but interesting to see how machine learning interprets the components and internal layouts of the device.
Real-World Insights and Experiences
- “The Snapdragon 855 SoC transformed my Galaxy S10 experience, especially in gaming and multitasking.” – User Review, Predictable Designs
- “I never knew the intricacies of the RF section in my phone until I had to switch carriers during my travel. The seamless connectivity across countries amazed me.” – Tech Enthusiast, Forum Discussion
- “After learning about the power management system in smartphones, I appreciate the engineering that goes into prolonging battery life.” – Smartphone User, Online Comment
Understanding the Basic Components

A basic digital cell phone includes a circuit board (the system’s brain), an antenna, an LCD, a keyboard, a microphone, a speaker, and a battery. These components work in unison to perform complex tasks and provide various functionalities like voice communication and digital data processing.
Exploring the Circuit Board
The heart of a cell phone is its circuit board, which includes:
- Analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog conversion chips
- A digital signal processor (DSP) for signal manipulation
- A microprocessor for managing the keyboard, display, and signaling
- Memory chips for storing the operating system and phone directory
- The RF and power section for managing power and FM channels
The Evolution of Displays in Cell Phones
The cell phone display has evolved significantly, offering features like built-in directories, calculators, games, and web browsers.
- Increased Functionality: Modern cell phone displays offer an array of functionalities, like web browsers and cameras.
- Growing Size: As features have expanded, so has the size of the displays, accommodating more apps and functionalities.
The Seamless Connectivity: SIM Cards
- SIM Integration: Some cell phones store critical information like the SID and MIN codes in internal flash memory, while others use external SIM cards.
- Speaker and Microphone Technology: Despite their tiny size, cell phone speakers and microphones deliver remarkable sound quality.